38 monocot leaf diagram
Diagram Of A Monocot Leaf Hibiscus Leaves, Hd Background Download, The Diagram, Leaf. L. Linaee Marx. 1 follower. More information. Hibiscus Leaves. 4. Presence of bundle sheath. (Leaf) (b) 1. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. 2. Absence, of cambium. 3. Presence of stomata on both the surfaces. 4. Vascular bundles are collateral and closed. 5. No differentiation of palisade and spongy parenchyma in mesophyll. (Isobilateral, monocot leaf) 2. Anatomy of Triticum - Leaf (Family ...
Monocot leaves are isobilateral as both the surfaces of the leaves are similar to the same coloration. The primordial monocot leaves consist of a proximal leaf base or hypophyll and a distal hyperphyll. The hyperphyll is the dominant part of the leaf in dicots, but in monocots, the hypophyll acts as the dominant structure.

Monocot leaf diagram
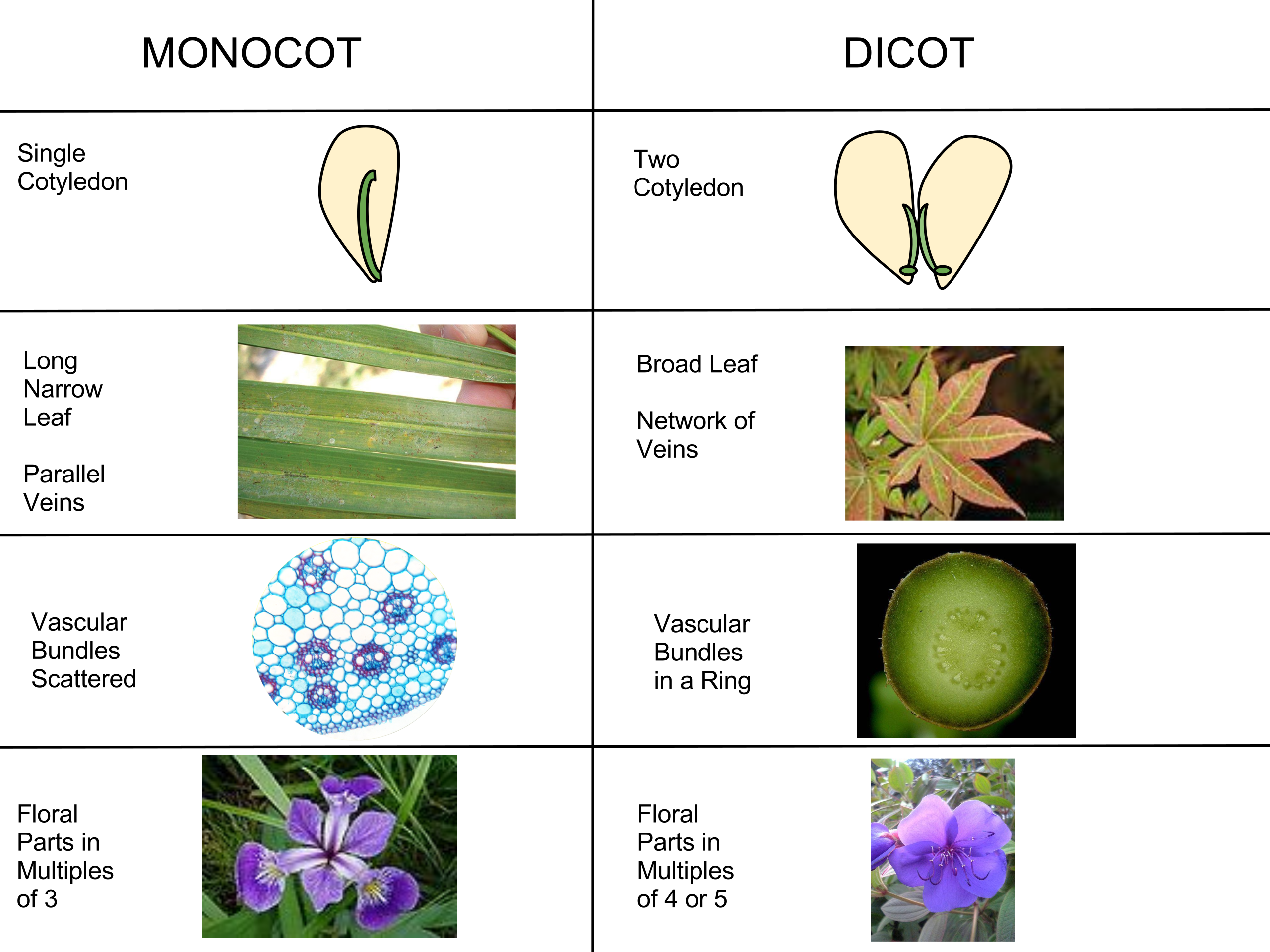
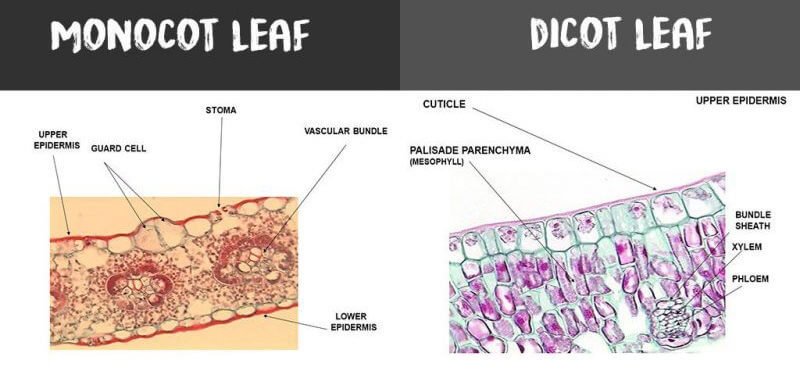
Difference Between Monocot Leaf and Dicot Leaf Historically, plants are classified into two categories based on the number of cotyledons or embryonic leaves. Therefore, the term "monocot" refers to the flowering plants that contain only one cotyledon. Leaf is the main place where photosynthesis occurs. Most leaves are usually green, due to presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. However, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll. In this article, learn the difference between monocot and dicot leaves. The basis of comparison include: […] In this tutorial, we have described Stem Anatomy (Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section). DICOT STEM CROSS SECTION For studying the internal structure of a typical dicot stem, the stem cross section of a young Sunflower or Cucurbita is taken. A thin transverse section of the stem reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epidermis It forms a single and the outermost layer of the ...
Monocot leaf diagram. Jun 6, 2007 — Monocot seeds have one "seed leaf" termed a cotyledon (in fact monocot is ... Diagram illustrating the tissue layers and their organization ... Answer (1 of 2): Vertical section of dicot leaf. Vertical section of monocot leaf Above diagram shows the kranz anatomy in C4 plants of monocots. Stomata of dicots and monocots. 1. Dicot leaves are dorsiventral in symmetry I. e they have dorsal and ventral surfaces; while monocots leases are ... Sep 20, 2017 - Anatomical Difference between Dorsiventral and Isobilateral Leaf. Compare the Anatomy of Dicot and Monocot Leaf with Comparison Table + Diagrams Anatomy Of A Dicot Leaf Sunflower Leaf. Solve This 81 The Diagram Given Below Represents The T S Of A. Plant Anatomy Biology4isc. Anatomy Of Monocot Leaves Botany. Monocot And Dicot Leafs With Diagram Plants. Schematic Transverse Section Through A Dicotyledon Leaf Indicating. Internal Structure Of Monocot Leaf Definition Examples Diagrams
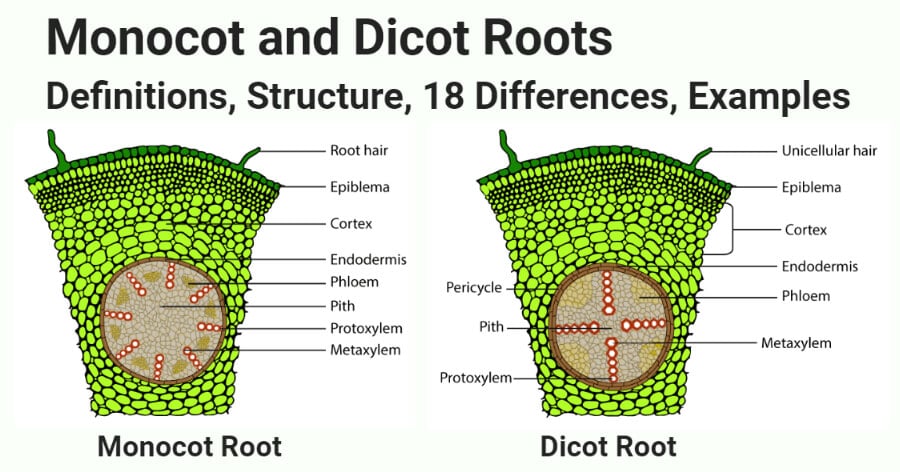
This article provides a diagram of monocot root. Also learn about: 1. Portion of transverse section of monocot root (arum) showing the plan of arrangement of. Monocotyledons commonly referred to as monocots are flowering plants ( angiosperms) whose seeds typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. Difference Between Dicot And Monocot Leaf With Comparison Chart Biology Reader ... the scientific diagram draw a labelled diagram of internal structure dicot leaf qs study draw a neat labelled diagram of t s dorsiventral leaf and describe the diffe parts sarthaks econnect largest online education community what is the difference between ts of ... Find monocot leaf stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. base of the leaf and are parallel to each other in each lobe of the leaf. If your plant is flowering, you can tell if it is a monocot or dicot by the number of petals and other flower parts. Monocots have flower parts in threes or multiples of threes as shown in the flowers to the left. Dicots have flower parts in multiples of fours or fives like
Anatomy of a Monocot Leaf - Grass Leaf . A transverse section of a grass leaf reveals the following internal structures. Epidermis . The leaf has upper and lower epidermis. They are made up of a single layer of thin walled cells. The outer walls are covered by thick cuticle. The number of stomata is more or less equal on both the epidermis. Monocot seeds have one "seed leaf" termed a cotyledon (in fact monocot is a shortening of monocotyledon). Dicots have two cotyledons. Both groups, however, have the same basic architecture of nodes, internodes, etc. Comparison of monocot (left, oat) and dicot (right, bean) gross anatomy. Monocot leaf is slender and long whereas dicot leaf is broader and comparatively smaller. Monocot leaf has even green color distribution while dicot leaf has a dark green color on the upper surface and light green on the lower surface. The venation of dicot leaf is reticulate whereas monocot leaf has parallel venation. Dicot Leaf Labeled Diagram. Schematic transverse section through a anatomy of a dicot leaf sunflower leaf monocot and dicot cross section draw a neat labelled diagram of t s. Schematic Transverse Section Through A Dicotyledon Leaf Indicating The Scientific Diagram. Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram Of T S Dorsiventral Leaf And Describe The Diffe ...
Zea mays (corn, a monocot) leaf cross section, 100X. The spongy mesophyll has air spaces for gas exchange and produces carbohydrates by photosynthesis. The upper and lower cuticle protect the leaf from water, sealing water inside and preventing excess rainwater from entering. The upper and lower epidermis produce the cuticle and protect the ...
Introduction Monocot leaves are the leaves that appear on plants produced from seeds with single cotyledon like Maize, Rice, Grass, Wheat, etc. Monocot leaves are said to be isobilateral leaves as both the surface of the leaves are with the same coloration. The leaves are usually ribboned like with parallel venation. Parallel venation means veins in the leaf are arranged in a parallel fashion.
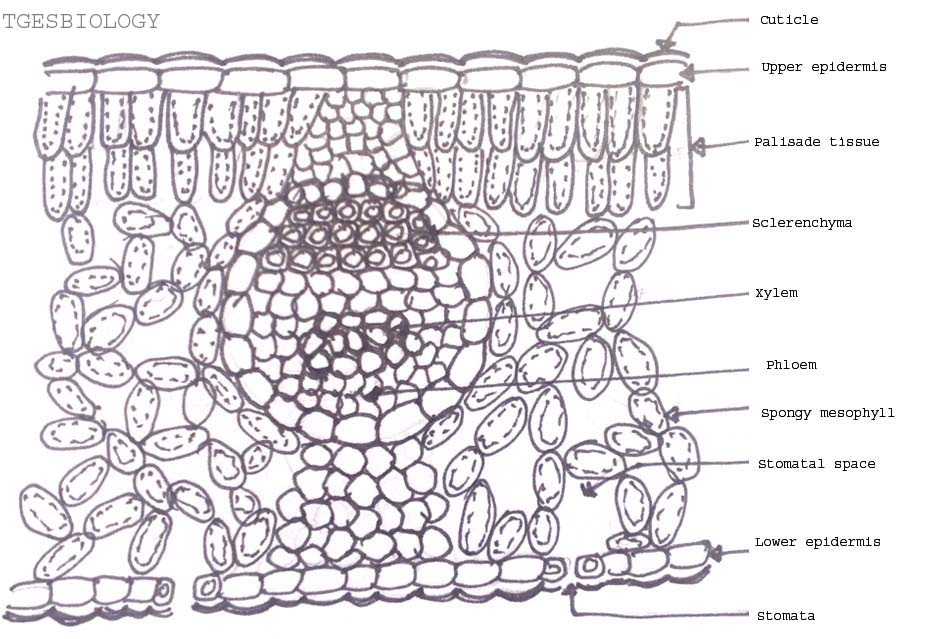
ABOUT DIAGRAM:Isobilateral leaf are found in monocotyledon (maize) which are usually erect. Internal structure consists of following characters:1. Epidermis:...
Main Difference - Stomata of Monocot vs Dicot Plants. Monocot and dicot plants contain stomata in their leaves as well as in their stem. The major role of stomata is to facilitate the gas exchange. They also facilitate transpiration, which helps the absorption of water from the soil and the transport of water through the xylem.The size of the stomata is controlled by a pair of guard cells.

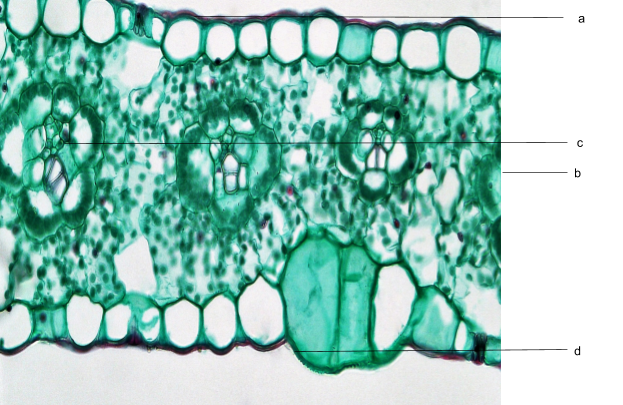
The Following Diagram Shows The T S Of Monocot Leaf Certain Parts Have Been Indicated By Alphabets Select The Option In Which A B C D E F And G Have Been Correctly
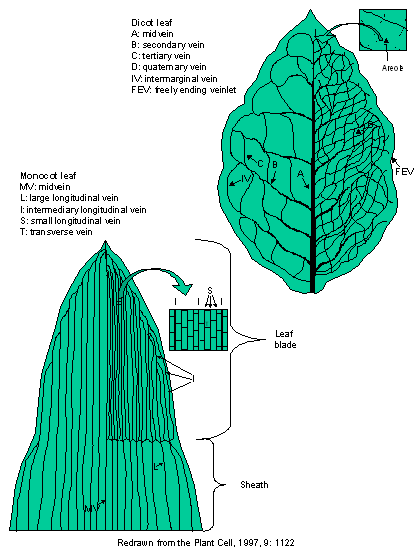
The main characteristic feature to distinguish the dicot and monocot leaf is the type of venation a leaf have. One can easily observe either the veins are striking or parallel by seeing a leaf. Below is the diagram of dicot and monocot leaf, where we can see the venation pattern.
Difference Between Dicot Leaf and Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaves. Monocot Leaves. Leaf Surface Characteristics. Dicots leaves have a dark green upper surface and a light green lower surface. No such differentiation. Both sides have the same colour. Size of Vascular Bundles.
Diagram via Plants Grow Here. Leaf Veins. Monocots tend to have parallel leaf veins (or venation), where the veins run parallel from the leaf stem (or petiole) to the tip, as seen on a blade of grass. Dicots tend to have reticulate leaf venation, where the veins branch off and laterally. There may or may not be one main vein (or midvein) that ...
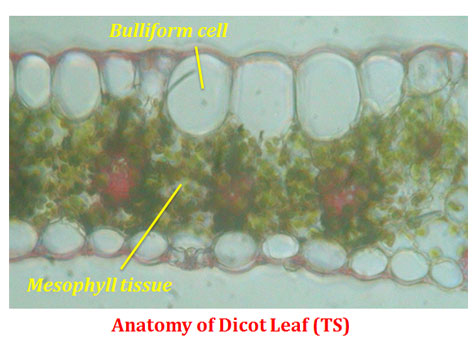
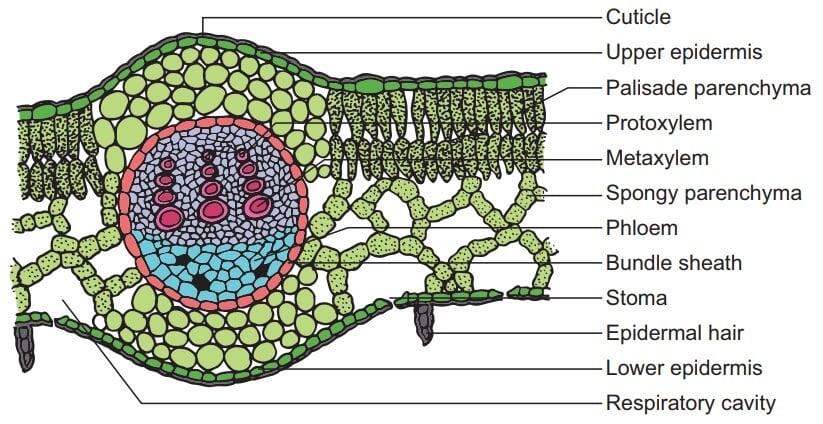
Leaf dermal tissue. Both monocot and dicot leaves have an outer, waxy layer called the cuticle that covers the dermal tissue of the upper and lower epidermis. The cuticle protects the leaf and helps it retain water. The epidermis, which is located beneath the cuticle, also protects the leaf.
Monocot's leaf or isobilateral leaf. Most of the monocot leaves are nearly erect and more or less both surfaces usually receive a direct and equal amount of sunlight. The internal structure of the monocot leaf shows the following anatomical structure. Epidermis: The epidermis is found on both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf.
Monocot Leaf Diagram Characteristics Of monocot Leaf. The guard cells of stomata are dumb-bell shaped in monocot leaf. The monocot leaf is slender and long in shape. The epidermal cells have almost straight lateral walls. The orientation of a monocot leaf can be described as isobilateral. Isobilateral orientation is whereby plant leaf surface ...
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot leafs. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf 2. Anatomy of Dicot Leaf. Monocot and Dicot Leaf: Type # 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf: Triticum-Leaf: ADVERTISEMENTS: T.S. shows prominent ridges and grooves and reveals the following tissues: Epidermis: 1. Two epidermal […]
Anatomy of Monocot Root (Monocot Root Cross Section Under Microscope with Diagram) Ø The anatomical features of a monocot root can be studied through a cross section (CS) through the root. Ø Anatomically, the monocot root has been differentiated into the following parts: (1). Epidermis (2). Cortex (3). Endodermis (4). Pericycle (5).
Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams. External Root Structure. Monocot Root. Dicot Root. External Structure of a Woody Stem. Monocot Stem. Woody Dicot Stem. Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaf.
The mesophyll of the monocot leaf is not clearly differentiated into two types, and air chambers are spread throughout. Also, the leaf veins look quite different in the monocot, although the xylem cells are still larger than the phloem cells. 3. Label the monocot leaf diagram in Figure 2 using the list of terms below. . Cuticle . Mesophyll ...
In this tutorial, we have described Stem Anatomy (Monocot and Dicot Stem Cross Section). DICOT STEM CROSS SECTION For studying the internal structure of a typical dicot stem, the stem cross section of a young Sunflower or Cucurbita is taken. A thin transverse section of the stem reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epidermis It forms a single and the outermost layer of the ...
Leaf is the main place where photosynthesis occurs. Most leaves are usually green, due to presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. However, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll. In this article, learn the difference between monocot and dicot leaves. The basis of comparison include: […]
Difference Between Monocot Leaf and Dicot Leaf Historically, plants are classified into two categories based on the number of cotyledons or embryonic leaves. Therefore, the term "monocot" refers to the flowering plants that contain only one cotyledon.

Point Pout The Differences In The Anatomy Of Leaf Of Peepal Ficus Religiosa And Maize Zea Mays Draw The Diagrams And Label The Differences






















Komentar
Posting Komentar