38 circular motion free body diagram
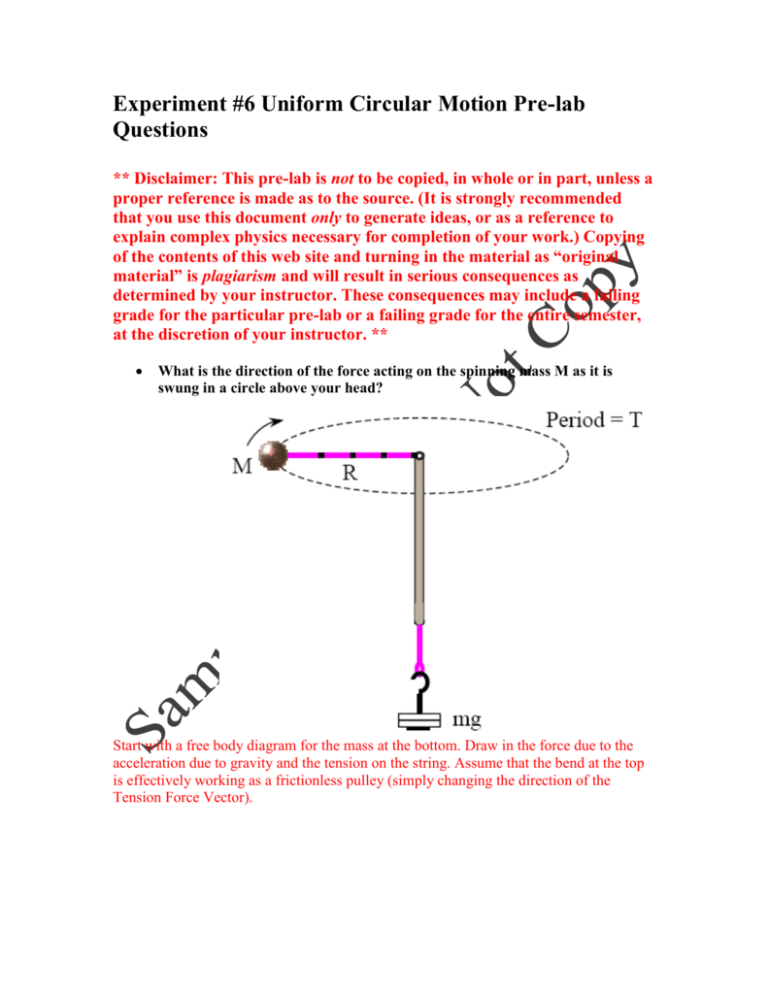
https://www.positivephysics.org/ produce this result. The classic example of nonuniform circular motion is an object rotating in a vertical circle in a gravitational field. Two examples are a bucket being swung around vertically on a rope, or a toy car doing a loop-to-loop. Let's draw the free-body diagram for an example such as this, specifically the swinging bucket. rope g ...
Have a look at the free-body diagram to evaluate the left-hand side, and write the right-hand side in the usual circular-motion form. This gives:. Solving for the normal force gives: . As long as the first term on the right exceeds the second term (in other words, as long as

Circular motion free body diagram
Check your understanding of free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion in this set of free practice questions aligned to AP Physics I standards. Rotational Motion 1. Draw a diagram of the object or objects that will be the system to be studied. 2. Draw a Free-body diagram for the object under consideration. 3. Identify the axis of rotation and determine the torques about it. Choose positive and negative directions of rotation, and assign the correct sign to each torque. 4. Laws of Motion; Circular Motion ©2011, Richard White www.crashwhite.com Part II. Free Response 6. A 500-kg race car is traveling at a constant speed of 14.0 m/s as it travels along a flat road that turns with a radius of 50.0m. a. Draw a free-body diagram for the car as it negotiates the right-turning curve. b.
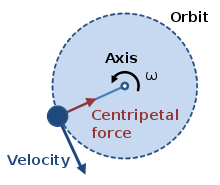
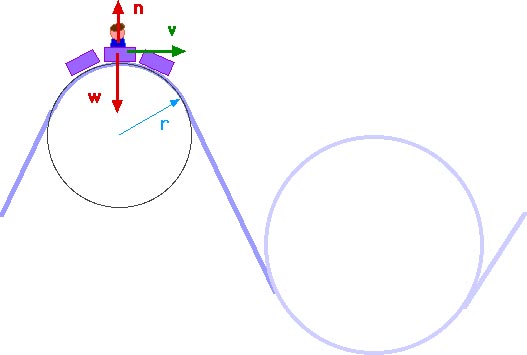
Circular motion free body diagram. Uniform circular motion. 9-29-99 Sections 5.1 - 5.2 ... You do NOT put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram for the same reason that ma does not appear on a free body diagram; F = ma is the net force, and the net force happens to have the special form when we're dealing with uniform circular motion. Let’s practice with free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion by drawing one for each position of the roller coaster. Remember, in this instance, there is only centripetal acceleration, no tangential acceleration. If there is a centripetal force causing centripetal acceleration, it must point to the center. the free-body diagram. The centripetal acceleration has to be provided by some other force (tension, friction, normal force) in order for circular motion to occur. 10 Circular Motion Lab from Rhett Allain on Vimeo. So, what are you going to do? First, the physics. If I were to draw free body diagram for the stopper at the above instant, it would look like this: There are only two forces on the stopper, the tension from the string and the gravitational force.
Students draw free-body diagrams of the object as it executes circular motion. 1.4 The student can use representations and models to analyze situations or solve problems qualitatively and quantitatively. Students use the free-body diagram and Newton's second law to write equations related to the motion of the object. 2.2 The student can apply The complete free-body diagram, in Figure 5.15, also shows an upward force of friction opposing the force of gravity. This force of friction is static friction because there is no relative motion between the person and the wall. Key ideas for circular motion: In uniform circular motion, there is a net force directed toward the center of the circle. AND Make a free body diagram for the stationary bob, i.e. when the spring and weight hanger over the pulley are attached. Discuss the net force, and Question : An apparatus that had a bob on it was used in a uniform circular motion lab so: Make a free body diagram for the bob while it is in uniform circular motion. Concept Question: Circular Motion and Force A pendulum bob swings down and is moving fast at the lowest point in its swing. T is the tension in the string, W is the gravitational force exerted on the pendulum bob. Which free-body diagram below best represents the forces exerted on the pendulum bob at the lowest point?
432 THE PHYSICS TEACHER Vol. 37, Oct. 1999 Free-Body Diagrams Revisited Free-Body Exercises: Circular Motion Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on the rock, and in each case, indicate the centripetal force. Please note that the rock is not in equilibrium if it is moving in a circle. The centripetal force depends on angular velocity ... How to draw a free-body diagram? 1, Please add vectors to create a free-body diagram. Assume that m1 is rotating at a speed v with a constant radius R. The following forces should be included in your free-body; Question: Circular motion lab question. How to draw a free-body diagram? 1, Please add vectors to create a free-body diagram. The motion of any particle in a circular path refers to "circular motion." A body is said to be in circular motion if it moves in a manner that the distance from a particular fixed point always remains same. In this topic, we will learn about dynamics of circular motion with its application. Free body diagram with circular motion Thread starter crybllrd; Start date Feb 27, 2010; Feb 27, 2010 #1 crybllrd. 120 0. Homework Statement In a circular rotating room (think Gravitron), there are two blocks stacked against the wall and do not drop. Block A is touching block B, and block B is touching the wall.
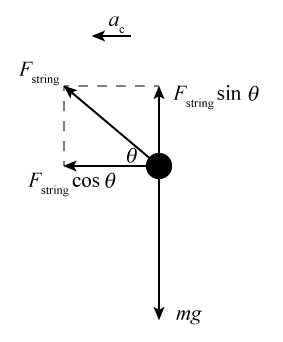
you should be able to maintain uniform circular motion. Figure 3a shows the free body diagram for the rotating bob in uniform circular motion. The weight of the mass is balanced by the tension in the suspending string. The centripetal force is provided by the tension in the spring attaching the bob to the shaft.
Free-body diagrams are covered in Senior 3 Physics. Notes to the Teacher Students can draw free-body diagrams to illustrate forces acting on a sphere or a coin moving in a uniform circular motion. In each case, they should indicate the force(s) responsible for the centripetal force. The relative length of the vectors
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion. The Forces in Circles Concept Builder provides learners with the challenge of identifying the free-body diagrams for situations involving the motion of objects in circles. Learners are presented with a short verbal description of an object's motion. They toggle through a set of free-body ...
10/23/2019 OA05: Forces and Circular Motion Correct Part B How fast must the bucket move at the top of the circle so that the rope does not go slack? Hint: draw a free-body diagram of the bucket at the top of the motion. ANSWER: Correct = 3.13 = 1.64
Free-Body Exercises: Circular Motion Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on the rock, and in each case, indicate the centripetal force. Please note that the rock is not in equilibljum if it is moving in a circle. The centripetal force depends on angular velocity and there may not be any indication of exactly how big that force should ...
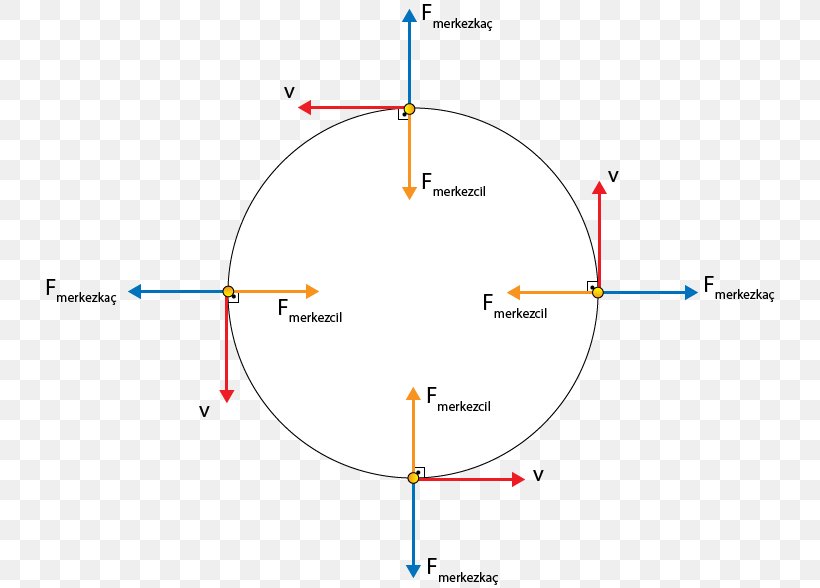
166 Chapter 7: Circular Motion & Rotation 7.02 Q: In the diagram below, a cart travels clockwise at constant speed in a horizontal circle. At the position shown in the diagram, which arrow indicates the direction of the centripetal acceleration of the cart? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 7.02 A: (A) The acceleration of any object moving in a circular ...
Demonstrating how to begin setting up a free-body diagram and equations for circular motion. Immediately follows "Free Body Diagrams and Newton's 2nd Law".
Circular motion, free-body diagram. Ask Question Asked 4 years, 8 months ago. Active 4 years, 8 months ago. Viewed 3k times 1 $\begingroup$ I having difficulty in explaining to my son the free-body diagram for following problem: A child flies a toy sphere attached at the end of a light elastic string. ...
Suggested Method of Solving Circular Motion Problems From the verbal description of the physical situation, construct a free-body diagram. Represent each force by a vector arrow and label the forces according to type. Identify the given and the unknown information (express in terms of variables such as m= , a= , v= , etc.).
Circular Motion in The Vertical Plane: Consider forces on the glass at the top of the circle Free body diagram for the glass v v. A ball with a weight of 2 N is attached to the end of a cord of length 2 meters. The ball is whirled in a vertical circle counterclockwise as shown below. The tension in the cord at the
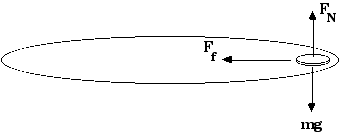
At rest, the free-body diagram is simple, with an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. These are the only two forces in the system even when circular motion is going on. The force of gravity has a constant magnitude and direction. The normal force, however, changes both magnitude and direction.
Laws of Motion; Circular Motion ©2011, Richard White www.crashwhite.com Part II. Free Response 6. A 500-kg race car is traveling at a constant speed of 14.0 m/s as it travels along a flat road that turns with a radius of 50.0m. a. Draw a free-body diagram for the car as it negotiates the right-turning curve. b.
Rotational Motion 1. Draw a diagram of the object or objects that will be the system to be studied. 2. Draw a Free-body diagram for the object under consideration. 3. Identify the axis of rotation and determine the torques about it. Choose positive and negative directions of rotation, and assign the correct sign to each torque. 4.
Check your understanding of free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion in this set of free practice questions aligned to AP Physics I standards.
![Circular Motion] Just need to know where to put the forces in ...](https://external-preview.redd.it/nVlgTuh7z3uMwMIvT7CNlV4hjWp3fpI3P_h_9gQp4ks.jpg?auto=webp&s=7f54eb8c74e8a91f3a3972ce8d09859ed8ee851d)




















Komentar
Posting Komentar