39 interstellar medium diagram
This diagram shows the location of the region near the Sun within 1500 light-years. The thin purple strips include the local interstellar cloud. The darkest regions have the lowest density of any type of gas. The Sun has been travelling for the last several million years through the Local Bubble a low density region of the interstellar medium. The interstellar extinction of starlight is the most indicative phenomenon revealing the pres- ... lar medium (ISM) is a steeply decreasing func-tion of size, n(a) ∝ a−3.5, extinction is gener- ... diagram has been obtained, the distance and the
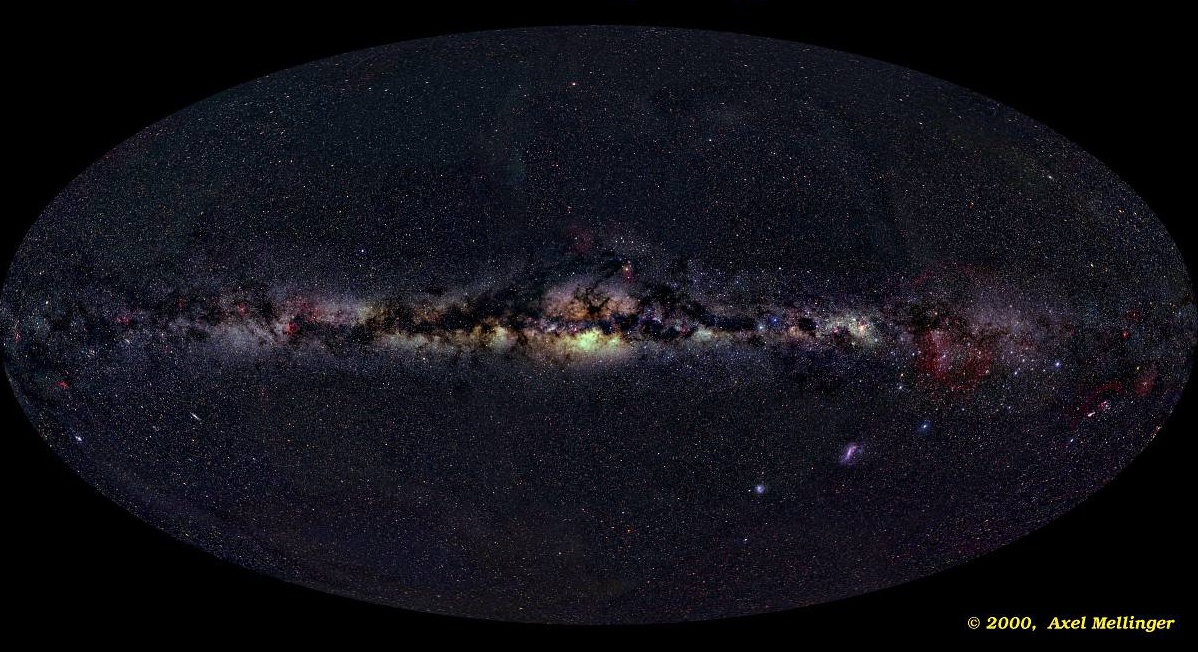
The Interstellar Medium Although space is very empty and the stars in the Milky Way are very far apart, the space between the stars contains a very diffuse medium of gas and dust astronomers call the interstellar medium (ISM). This medium consists of neutral hydrogen gas (HI), molecular gas (mostly H 2 ), ionized gas (HII), and dust grains.
Interstellar medium diagram
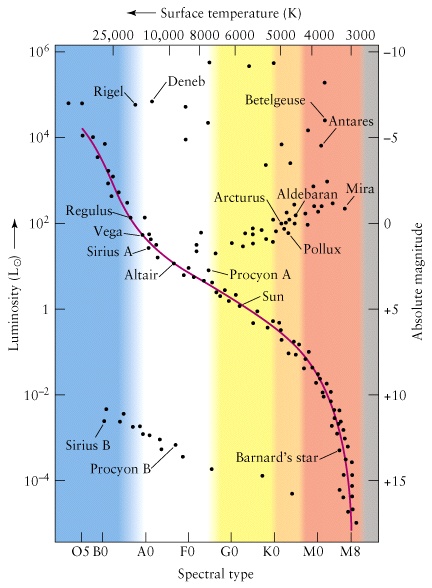
Populations of stars co-evolve with the interstellar medium in which they form. This highly simplified diagram shows the flow of material as giant stars evolve into supernovas which enrich molecular clouds with metals that they synthesized which are then inherited by the next generation of stars. The interstellar medium is far too cool to excite the higher energy states of hydrogen, but there is a feature at the 21 centimeter (cm) wavelength in the radio frequency. 21-cm photons are produced by the spinning magnetic fields of the hydrogen atom's nuclear proton and orbiting electron. By plotting stars on this diagram, astronomers were able to see patterns, which in turn helped them understand more about how stars changed throughout their life cycle. Interstellar Medium The Interstellar Medium is made up of small particles of dust and gas that exists in the space between stars.
Interstellar medium diagram. The interstellar medium consists of low-density gas and dust. Interstellar gas consists of cool clouds embedded in hot intercloud gas. The interstellar medium emits, absorbs, and reflects radiation. (1) The interstellar medium (that's just a fancy name for the matter between stars) consists of low-density gas and dust. Download scientific diagram | 4 Schematic view of the dominant physico-chemical processes in the interstellar medium depending on the physical conditions from publication: Astrochemistry ... Because interstellar medium is 97% hydrogen and 3% helium, with trace amounts of dust, etc., a star primarily burns hydrogen during its lifetime. A medium-size star will live in the hydrogen phase, called the main sequence phase, for about 50 million years. Once hydrogen fuel is gone, the star has entered "old age." The interstellar medium consists of gas and dust. Atoms, mostly hydrogen and helium, and small molecules make up the gas. The dust is more like clumps of soot or smoke (and ice?). Dust absorbs light and reddens light that gets through by scattering. This image shows distinct reddening of stars near the edge of the dust cloud
Stars form when an interstellar cloud collapses under its own gravity, heats, and breaks into pieces of star-sized masses. The evolution of the protostar can be represented as a path on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The resulting protostar, which emits primarily infrared radiation is known as a T Tauri star. The interstellar medium is a true vacuum. True False . In stars, the pressure generated from fusion balances the inward a force of gravity. ... one red and one blue, on the HR diagram, what will you see? The red star is moving closer to the Earth while the blue star moves farther away. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Interstellar extinction and the reddening of light by the interstellar medium (ISM) are both caused by _____. only dust in the ISM ... Eighty percent of the stars on the H-R diagram are on the main sequence, and that is because the star is in hydrostatic equilibrium due to the _____.
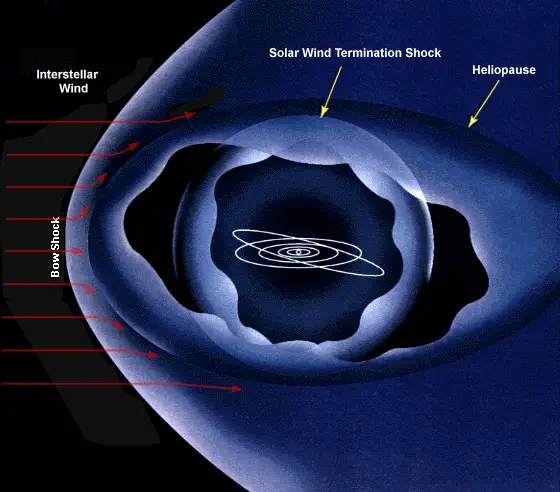
the path that a protostar follows on the HR Diagram as it contracts toward the main sequence. Intercloud Gas. a low-density region of the interstellar medium that fills the space between interstellar clouds. Interstellar Cloud. a discrete, high-density region of the interstellar medium made up mostly of atomic or molecular hydrogen and dust ... Where does a 1 solar-mass protostar appear on an H-R diagram? ... What do we mean by the interstellar medium? the gas and dust that lies in between the stars in the Milky Way galaxy. The interstellar clouds called molecular clouds are _____. the cool clouds in which stars form. The solar wind changes with the 11-year solar cycle, and the interstellar medium is not homogeneous, so the shape and size of the heliosphere probably fluctuate. The solar magnetic field is the dominating magnetic field within the heliosphere, except in the immediate environment of planets which have their own magnetic fields. Diagram of the solar system showing planets, heliopause, and interstellar space. The numbers shown are astronomical units ( AU ), where 1 AU is the distance between the sun and the Earth. Image via...
• The interstellar medium (ISM) consists of gas and dust existing over a wide range of physical conditions • About 1/2 of the ISM mass in our Galaxy is molecular in form • The ISM is powered by energy emitted by stars (SN, giant stars, novae, etc.) • The 5 ISM components: "coronal" gas, warm intercloud medium (WIM), HII regions,
Mastering Astronomy Chapter: 11. As a clump of interstellar gas contracts to become a main-sequence star, its changing position on the H-R diagram tells us __________. Watch the red dot representing the protostar in the animation.
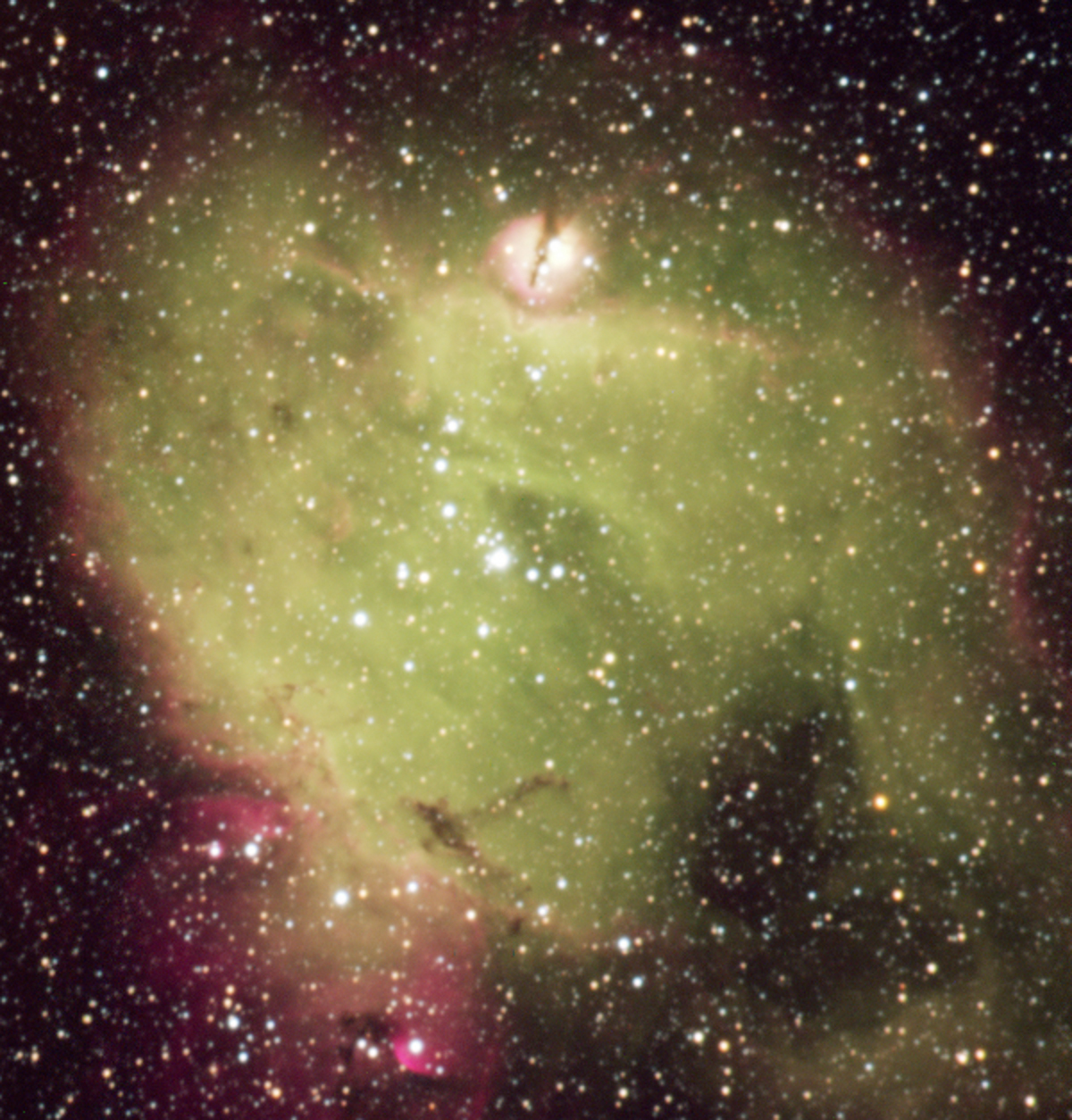
Astronomers refer to all the material between stars as interstellar matter; the entire collection of interstellar matter is called the interstellar medium (ISM).Some interstellar material is concentrated into giant clouds, each of which is known as a nebula (plural "nebulae," Latin for "clouds"). The best-known nebulae are the ones that we can see glowing or reflecting visible light ...
Large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) molecules carry the infrared (IR) emission features that dominate the spectra of most galactic and extragalactic sources. This review surveys the observed mid-IR characteristics of these emission features and summarizes laboratory and theoretical studies of the spectral characteristics of PAHs and the derived intrinsic properties of emitting ...
This paper presents a simple model of the interstellar medium based on supernova domination and characterized by mechanical heating of H I regions and radiative cooling of the hottest material via a galactic fountain. A phase diagram of the H I material is derived and from it a feedback mechanism, based on the stability criterion for "intercloud" (i.e., T ∼ 104 K) material, is ...
Interstellar medium diagram. Dust - Dark clouds reflection nebulae and Bok globules. Some interstellar material is concentrated into giant clouds each of which is known as a nebula plural nebulae Latin for clouds.
Interstellar Extinction:. Astrophotograph in the 19th century showed that the dark lanes or holes in the Milky Way did not have sharp edges. That, in fact, detail studies of star clusters at various distances from us showed that the intensity of light from remote stars is reduced as it passes through the sparse material of the interstellar medium.
Abstract. Although most of the mass of the Milky Way Galaxy is condensed into stars, interstellar space is not completely empty. It contains gas and dust, in the form both of individual clouds and of a diffuse medium.Interstellar space typically contains about one gas atom per cubic centimetre and one dust particle in 100000 cubic centimetres.
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun.It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space.In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium.The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind.
Where does a 1-solar-mass protostar appear on an H-R diagram? to the right of the main sequence, and higher up than the Sun. ... What do we mean by the interstellar medium? the gas and dust that lies in between the stars in the Milky Way galaxy. The interstellar clouds called molecular clouds are.
The diagram doesn't show the solar wind, but it travels outward in all directions from the Sun, which is the only reason there is a heliosphere. What you see on the right isn't actually a sphere (in spite of the diagram), since it fills space and surrounds the heliosphere on all sides; that means the heliosphere is a kind of extended atmosphere ...
By plotting stars on this diagram, astronomers were able to see patterns, which in turn helped them understand more about how stars changed throughout their life cycle. Interstellar Medium The Interstellar Medium is made up of small particles of dust and gas that exists in the space between stars.
The interstellar medium is far too cool to excite the higher energy states of hydrogen, but there is a feature at the 21 centimeter (cm) wavelength in the radio frequency. 21-cm photons are produced by the spinning magnetic fields of the hydrogen atom's nuclear proton and orbiting electron.
Populations of stars co-evolve with the interstellar medium in which they form. This highly simplified diagram shows the flow of material as giant stars evolve into supernovas which enrich molecular clouds with metals that they synthesized which are then inherited by the next generation of stars.





























Komentar
Posting Komentar