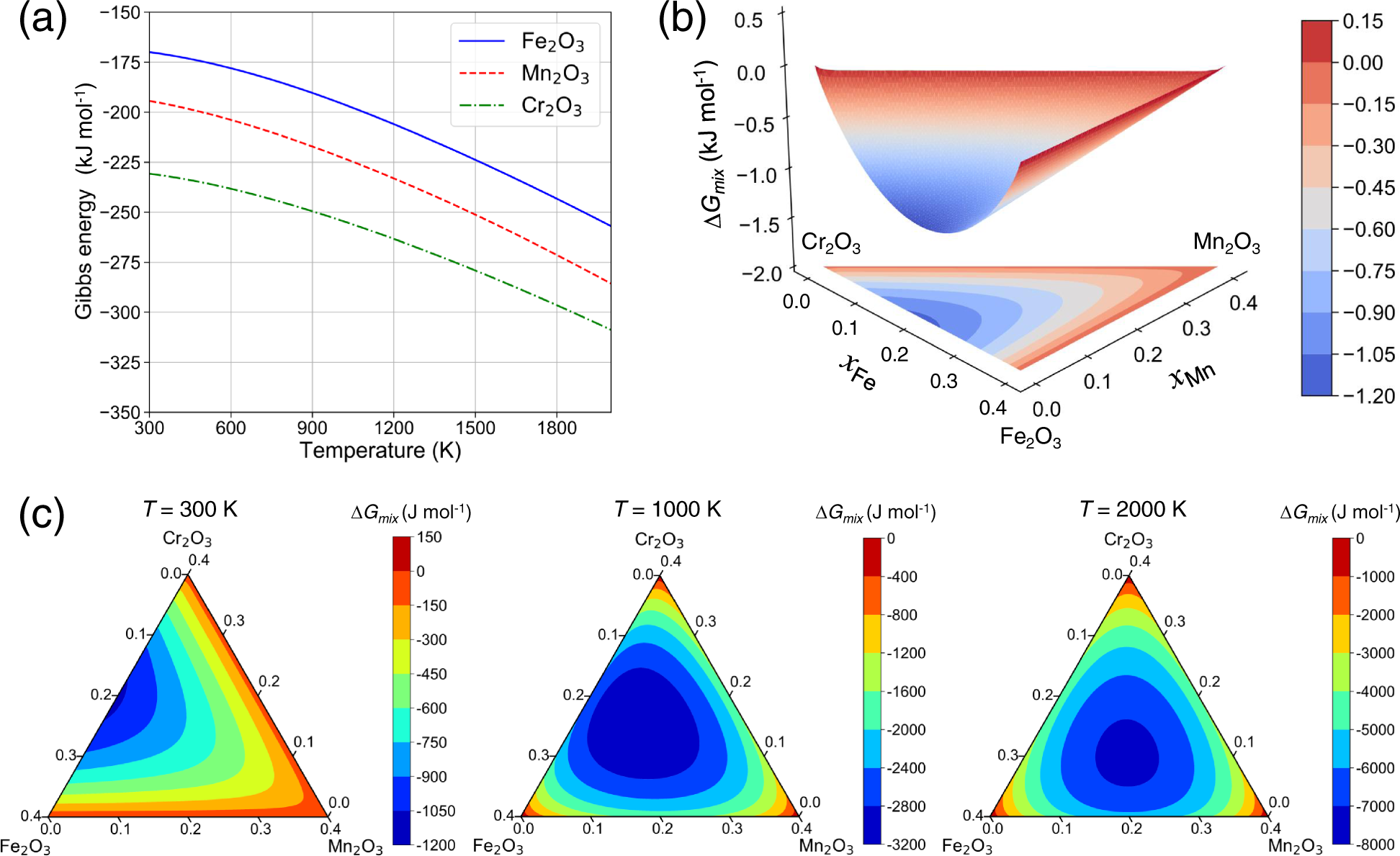
39 pourbaix diagram iron
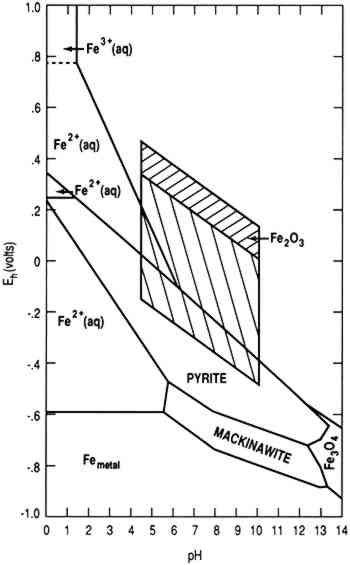
FeS2 is Marcasite structured and crystallizes in the orthorhombic Pnnm space group. The structure is three-dimensional. Fe3+ is bonded to six equivalent S+1.50- atoms to form a mixture of edge and corner-sharing FeS6 octahedra. Pourbaix diagram of iron. In electrochemistry, and more generally in solution chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, EH-pH diagram or a pE/pH diagram, is a plot of possible thermodynamically stable phases ( i.e., at chemical equilibrium) of an aqueous electrochemical system. Boundaries (50 %/50 %) between the ...
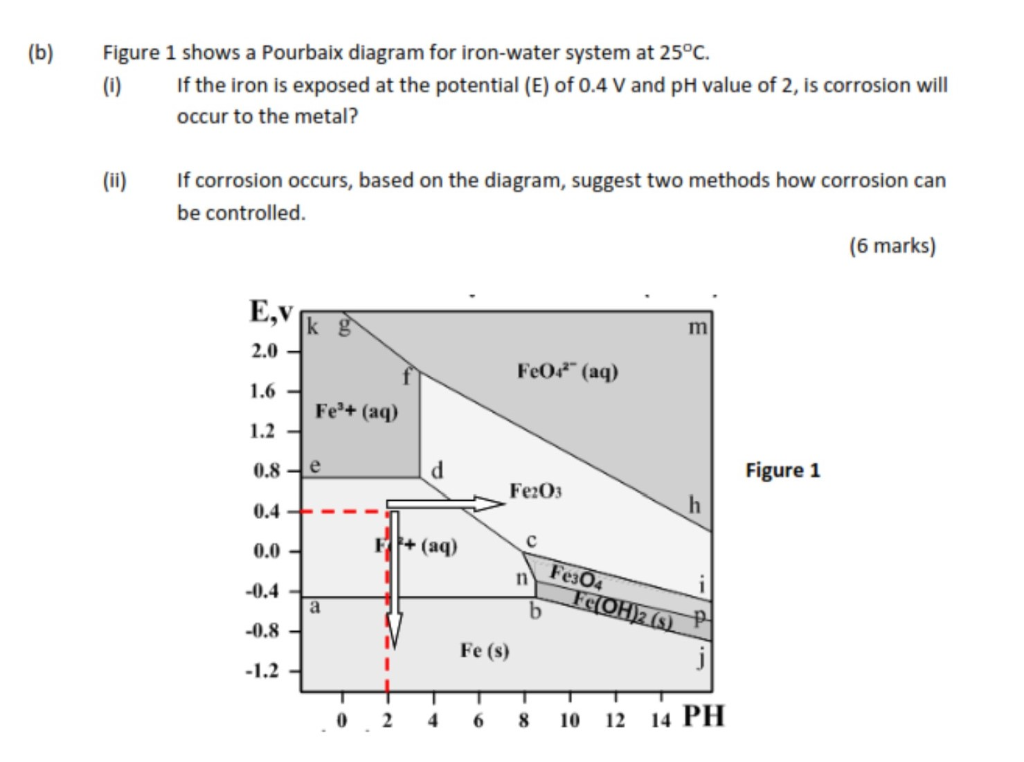
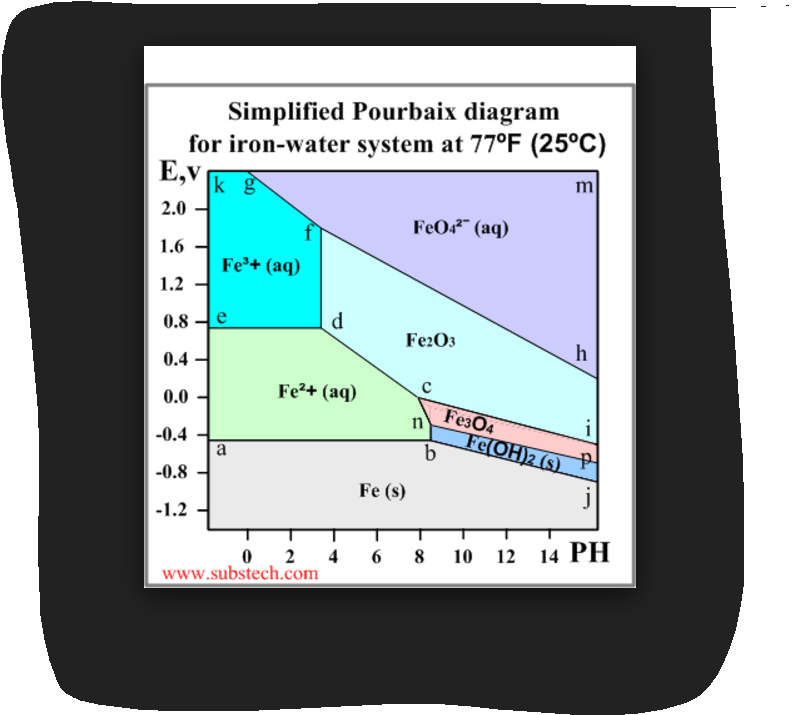
On the Pourbaix diagram for iron find: the chemical form of iron that is the strongest oxidizing agent. the form of iron that is the strongest reducing agent the form of iron that would predominate in a neutral solution at a potential of 0.00V the standard reduction potential for the reduction of Fe 2+ to Fe metal

Pourbaix diagram iron
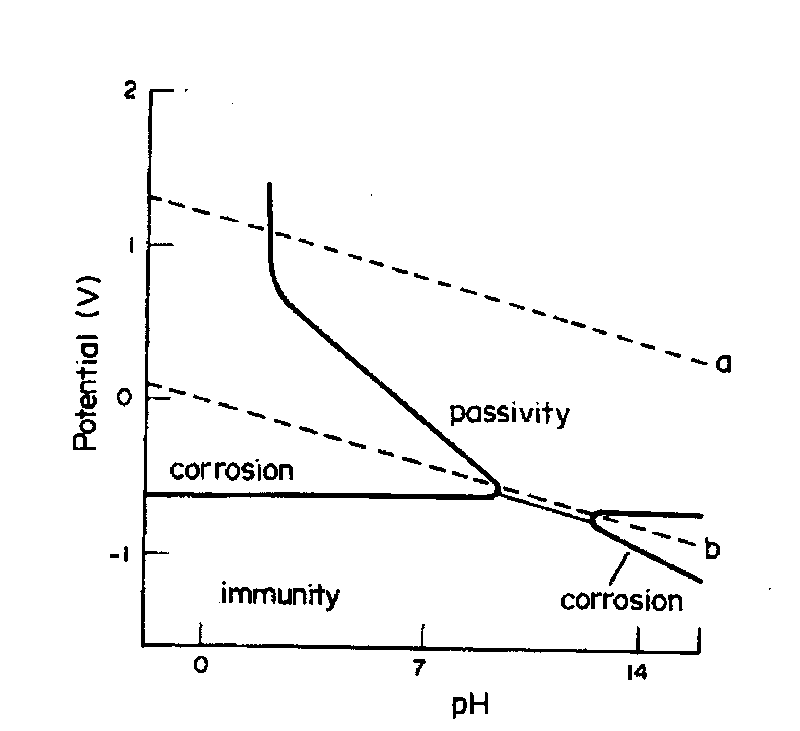
Pourbaix Diagram of Iron at 25 o C. The following diagram, produced with the KTS Thermo Excel add-on and modified for the Internet, describes the potential-pH equilibrium diagram for the system iron-water at 25 o C considering only the hydrated forms of the possible s. The gray zone describes the region of stability of the base metal (Fe or iron), also called the immunity region according to ... The Pourbaix diagram is, therefore, in no way a state space that fully describes the state of the steel surface/electrolyte system, as suggested in Figure 8 in a recent publication. 3 This cannot be expected from a diagram that is only defined along the thermodynamic equilibrium lines. The Pourbaix diagrams for iron show a base metal, as the immunity region is situated below the hydrogen-water line, Figs 2 and 3. However, iron can passivate in slightly alkaline solutions, where a solid layer protects the metal from further dissolution (the ideal case). Acidic solutions dissolve iron and form Fe2+(aq) with hydrogen evolution.
Pourbaix diagram iron. The Pourbaix diagram can be thought of as analogous to a phase diagram of an alloy, which plots the lines of equilibrium between different phases as temperature and composition are varied. To plot a Pourbaix diagram the relevant Nernst equations are used. As the Nernst equation is ignored, although the diagram is slightly dependent on these species. b The two states of the metal in Pourbaix diagrams are dissolved (as ions) or solid, including metal: metal oxide(s), hydroxides and oxy-hydroxides. For iron, the important species are the ions Fe2+, Fe3+, Fe(OH)2+, Fe(OH)− 3 and FeO 2− 4 and the solids Fe, Fe3O4 and Fe2O3. Pourbaix diagram (Electrode potential / PH diagram) is a graphical An example of a Pourbaix diagram for the system iron-water is presented. and simple. Mod-01 Lec-07 Pourbaix diagram This gives enough information for a simple Pourbaix diagram This example - basic oxidation/reduction reactions for aqueous systems. 13.04.2021 · Pourbaix diagram for iron. Three oxidation states of iron (0, +2 and +3) are represented on this diagram. The stability regions for the oxidized iron states are shown only within the stability region of H 2 O. Equilibria between species separated by vertical lines are dependent on pH only. The +3 oxidation state is the only stable one in environments in which …
Pourbaix [4] in the form of potential–pH diagrams, as shown for iron corrosion in Figure 1.1. The corrosion of metallic iron may occur in the potential–pH region where hydrated ferrous ions Fe2+, ferric ions Fe3+, and hydroxo-ferrous ions Fe(OH)− 3 are stable. No iron corrosion occurs in the region where metallic iron is thermodynamically stable at relatively negative electrode ... Pourbaix diagrams show solid-aqueous phase stability as a function of pH and redox potential and can be a valuable tool to guide the hydrothermal synthesis of transition metal oxides. However, the Pourbaix diagram is based on thermodynamics, and nucleation kinetics are not readily apparent in this framework. Interpretation of the Pourbaix Diagram About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
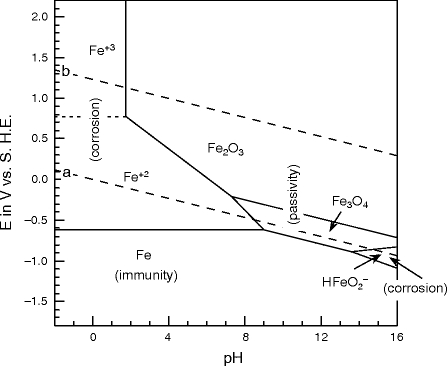
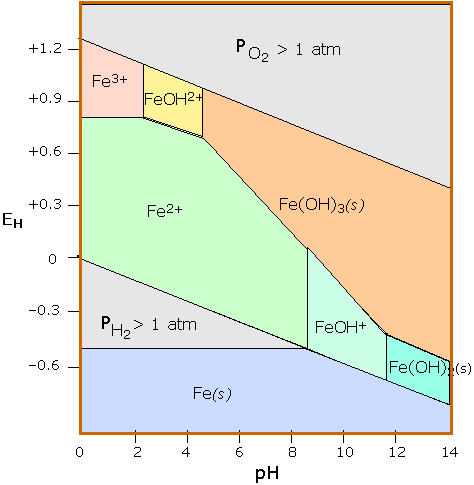
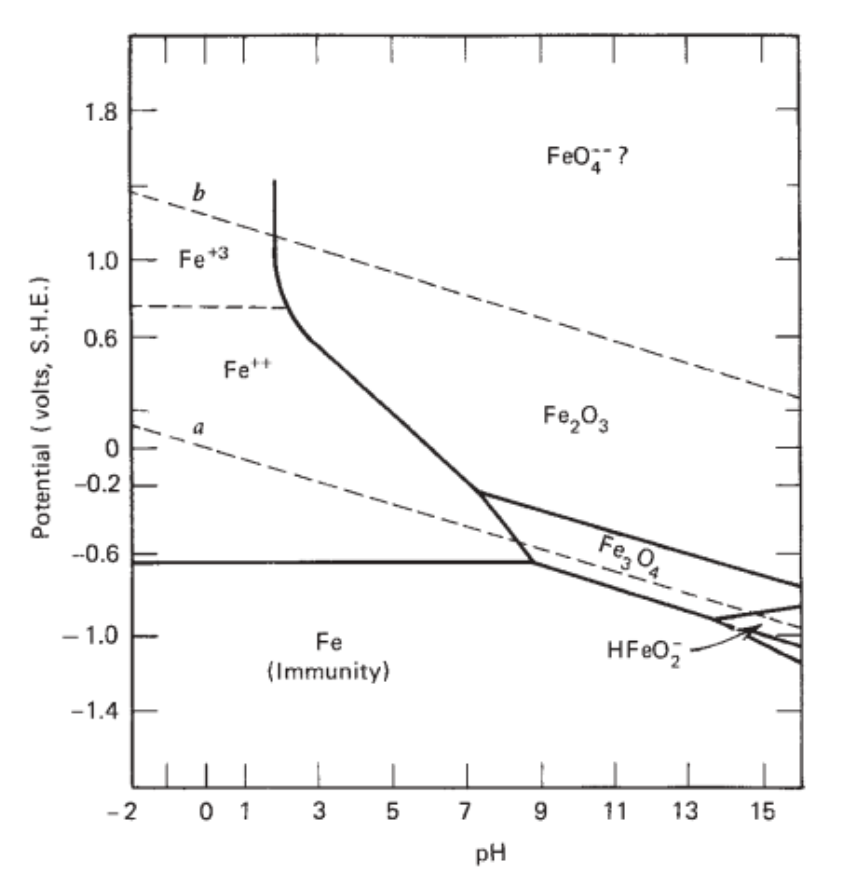
The Pourbaix diagram for the iron water system shows the most thermodynamically stable species occurring at various potentials and pH, when the system is under equilibrium. Zoom In Zoom Out Reset image size Figure 2. Replicated Pourbaix ... Calculated Pourbaix diagram for iron in neutral to alkaline environment. Varying concentrations (log(mol/L)) of dissolved ions influence the stability regions. Potentials with respect to Cu/CuSO4. … Pourbaix diagram of aqueous iron. Outside chemistry, "ferrous" means generally "containing iron". The word is derived from the Latin word ferrum ("iron"). Ferrous metals include steel and pig iron (with a carbon content of a few percent) and alloys of iron with other metals (such as stainless steel). "Non-ferrous" is used to describe metals and alloys that do not contain an … A potential-pH diagram for iron (Pourbaix diagram) shown in Fig. 1 indicates the areas of immunity, passivity and corrosion of iron in the function of potential and pH. Four separate areas-regions ...
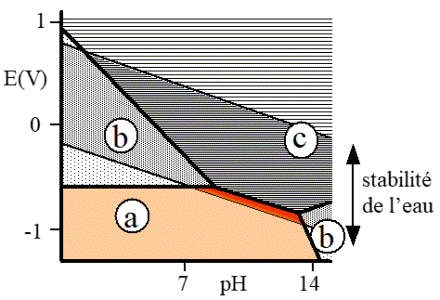
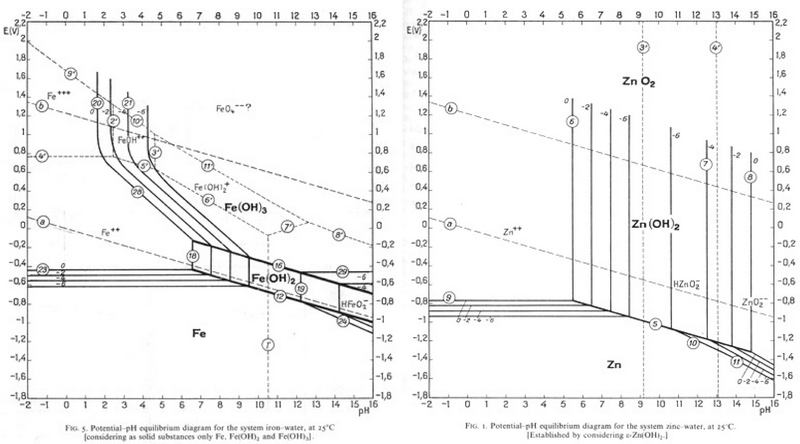
Normally the Poubaix diagrams are built for the water solutions with the concentrations of metal ions 10-6 M and at the temperature 298K (77ºF/25ºC). An example of a Pourbaix diagram for the system iron-water is presented in the picture. The diagram defines the following zones of the equilibrium states:
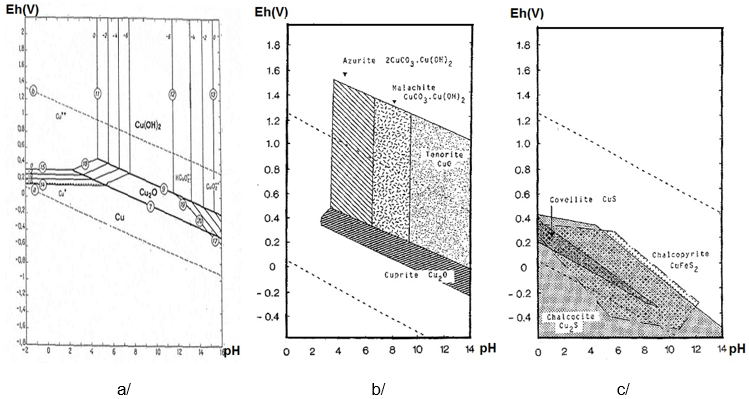
Cr2O3 is Corundum structured and crystallizes in the trigonal R-3c space group. The structure is three-dimensional. Cr3+ is bonded to six equivalent O2- atoms to form a mixture of edge, corner, and face-sharing CrO6 octahedra. The corner-sharing octahedra tilt angles range from 47–61°. There are three shorter (2.01 Å) and three longer (2.06 Å) Cr–O bond lengths.
Stability-field diagram for aqueous ferric-ferrous system _.__ 5 ... Iron is relatively abundant in the earth's crust. Rankama and ... Pourbaix, 1949.
25.2 Pourbaix Diagrams reactions of metals. When iron metal is exposed to acidic/neutral/basic solutions, several reactions can The electrode potentials of the metal, E and the pH of the surrounding medium are the main factors or parameters that determine the stability of the solid phases and the ionic species produced during redox occur.
Development of the Materials Project is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) through its Office of Science, via the Basic Energy Sciences (BES) and Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) programs, and through its Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), via the Battery Materials Research (BMR, formerly BATT) program.
originator, Pourbaix (1963), a Belgium electrochemist and corrosion scientist. These diagrams represent the stability of a metal as a function of potential and pH. at a particular combination of pH and potential, a stable phase can be determined from the Pourbaix diagram. In such diagrams, the redox potential of the corroding system is
Below is the Pourbaix diagram for aqueous solutions of iron. Notice that not all lines are horizontal or vertical. Each line represents a set of conditions ( E 0 and pH) where two ionic species are in dynamic equilibrium. For example, at E 0 = 1.0 V and pH = 2, the predominating species is F e X 3 + ( a q).
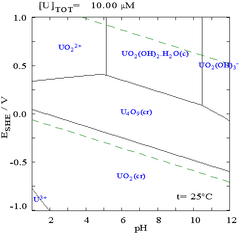
The Pourbaix diagrams at [I] = 10 −2 M are also useful for the experimental synthesis of related compounds through solution precipitation, where a relatively high [I] should be required (DFT ...
A Pourbaix diagram, also frequently called a potential-pH diagram, or E-pH diagram, is a representation of aqueous phase electrochemical equilibria. It is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional free energy-pH-potential diagram. In other words, it shows water-stable phases as a function of pH and potential, where, potential is ...
A Pourbaix diagram is a plot of the equilibrium potential of electrochemical reactions against pH. It shows how corrosion mechanisms can be examined as a function of factors such as pH, temperature and the concentrations of reacting species. Background Electrode potentials.
by the Pourbaix diagrams to those formed during experiments. It was observed that the experimental results generally agreed with the predictions made by the Pourbaix diagrams. Keywords: Hydrogen sulfide, iron sulfide, Pourbaix diagram, polymorphous, H2S corrosion, thermodynamic INTRODUCTION
Fe-pourbaix-diagram.svg. Pourbaix diagram of iron in uncomplexed media (anions other than OH - not considered). Ion concentration 0.001 m (mol/kg water). Temperature 25°C. Date. 23 October 2007. Source. self-made, with data from software FactSage version 5.3. Author.
The Pourbaix diagram is a projection of the equilibrium potential surface in a many dimensional parameter space onto the subspace of pH. When other conditions deviate from the standard conditions, the equilibrium potential curve will also move on the Pourbaix diagram. 3. To correctly interprete the Pourbaix diagrams, we should first locate the ...
English: Pourbaix diagram of Iron; c(Fe) = 10^-6 mol/l, T = 25 °C. Bahasa Indonesia: Diagram Pourbaix besi; c(Fe) = 10^-6 mol/l, T = 25 °C. Source own work This W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Inkscape . Data Source University of Bath & Western Oregon University. Date 2006-09-27
The Pourbaix diagram for the iron-water system at 25°C shown in Fig. 2 10 suggests that steels should form protective oxide films, probably composed of magnetite (Fe 3 O 4), at pH up to ~14, approximately equivalent to ~4% (w/w), or 1 M, sodium hydroxide.
Thermodynamics: Pourbaix Diagrams. R. Winston Revie, Senior Research Scientist. CANMET Materials Technology Laboratory, Natural Resources Canada. Search for more papers by this author. Herbert H. Uhlig, Former Professor Emeritus. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA.
Fe3O4 is Spinel-derived structured and crystallizes in the trigonal R-3m space group. The structure is three-dimensional. there are three inequivalent Fe+2.67+ sites. In the first Fe+2.67+ site, Fe+2.67+ is bonded to six O2- atoms to form FeO6 octahedra that share corners with six equivalent FeO4 tetrahedra and edges with six FeO6 octahedra.
Iron(III) and Life. All known forms of life require iron. Many proteins in living beings contain bound iron(III) ions; those are an important subclass of the metalloproteins.Examples include oxyhemoglobin, ferredoxin, and the cytochromes.. Almost all living organisms, from bacteria to humans, store iron as microscopic crystals (3 to 8 nm in diameter) of iron(III) oxide hydroxide, …
Iron E-pH (Pourbaix) Diagram. The following Figure illustrates the E-pH diagram for iron in the presence of water or humid environments at 25 o C, which was calculated by considering all possible reactions associated with iron in wet or aqueous conditions listed in the Table below, excluding therefore drier forms of corrosion products such as magnetite (Fe 3 O 4) or iron (ferric) oxide (Fe 2 O 3).
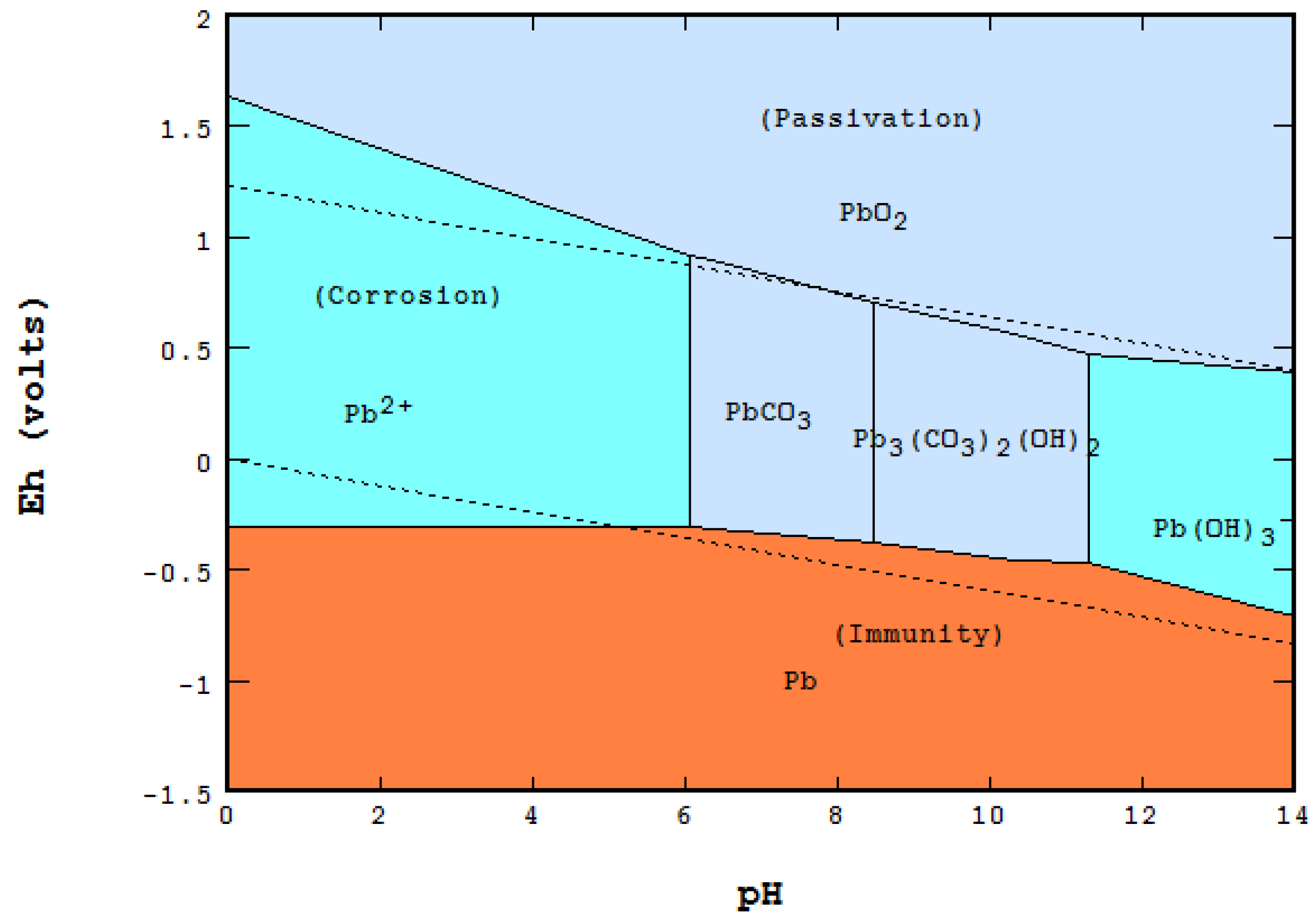
The corrosion of iron (and other active metals such as Al) is indeed rapid in parts of the Pourbaix diagram where the element is oxidized to a soluble, ionic product such as Fe 3+ (aq) or Al 3+ (aq). However, solids such as Fe 2 O 3 , and especially Al 2 O 3 , form a protective coating on the metal that greatly impedes the corrosion reaction.
The Pourbaix diagrams for iron show a base metal, as the immunity region is situated below the hydrogen-water line, Figs 2 and 3. However, iron can passivate in slightly alkaline solutions, where a solid layer protects the metal from further dissolution (the ideal case). Acidic solutions dissolve iron and form Fe2+(aq) with hydrogen evolution.
The Pourbaix diagram is, therefore, in no way a state space that fully describes the state of the steel surface/electrolyte system, as suggested in Figure 8 in a recent publication. 3 This cannot be expected from a diagram that is only defined along the thermodynamic equilibrium lines.
Pourbaix Diagram of Iron at 25 o C. The following diagram, produced with the KTS Thermo Excel add-on and modified for the Internet, describes the potential-pH equilibrium diagram for the system iron-water at 25 o C considering only the hydrated forms of the possible s. The gray zone describes the region of stability of the base metal (Fe or iron), also called the immunity region according to ...
![Pourbaix Diagrams for Iron - [PDF Document]](https://reader015.fdocuments.in/reader015/html5/0308/5aa0231cf09f6/5aa0231e5c2aa.png)


![PDF] Construction And Verification of Pourbaix Diagrams For ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/25421101b5d7ad717197f0a0c51bb4d86ce0eb9b/6-Figure1-1.png)
![PDF] Construction and Verification of Pourbaix Diagrams for ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/41856ae950ec477e6783e072ac6a0a40160361a8/11-Figure8-1.png)











Komentar
Posting Komentar