40 diagram of covalent bond
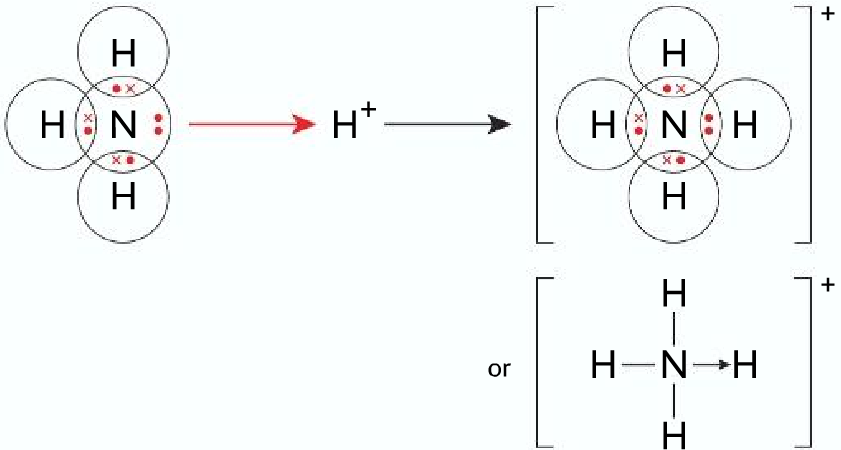
One coordinate bond in which both electrons are donated from the N atom to the B atom 4. One coordinate bond in which both electrons are donated from the O atom to the C atom 5. No coordinate bonds (1 mark for each correct dot and cross diagram; 1 mark for correct identification of the coordinate bond or the lack of coordinate bond) 3.2.2. The energy band diagram of a p-type Semiconductor is shown below: A large number of holes or vacant space in the covalent bond is created in the crystal with the addition of the trivalent impurity. A small or minute quantity of free electrons is also available in the conduction band.
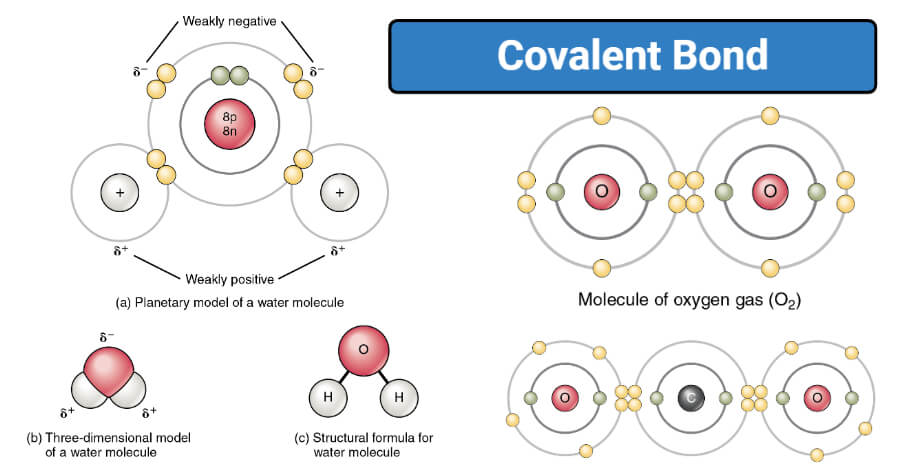
Coordinate Covalent Bonds. A coordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. A covalent bond is formed by two atoms sharing a pair of electrons. The atoms are held together because the electron pair is attracted by both of the nuclei.

Diagram of covalent bond
A covalent bond can be represented by a straight line or dot-and-cross diagram. Water formula is presented in diagram covalent bond takes place between two hydrogen. Covalent bonds are directional where the atoms that are bonded showcase specific orientations relative to one another. Each dot structure covalent lewis bonds lewis dot diagram. Some of the worksheets for this concept are lewis dot structures and molecule geometries work covalent bonding work bonding basics chapter 7 practice work covalent bonds and molecular covalent ws lewis structures covalent practice problems h s so ch br hcn. 4. Fulfill all atoms octet by making a covalent bond. In this step, we will use a covalent bond to fulfill the octet of atoms if necessary. As in the 3rd step structure, Carbon not getting what it needs, so, simply convert the lone pair on nitrogen to a covalent bond.
Diagram of covalent bond. relates to covalent bonding. add circles if necessary. eXtension draw a cluster diagram for each type of bond. Lesson summary the octet rule in covalent Bonding Covalent compounds are most stable when each atom has eight electrons. Single, double, and triple covalent bonds depend on the number of pairs of electrons shared between two atoms. A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 0.4 and 1.7 is called a polar covalent bond. A polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the atoms have an unequal attraction for electrons and so the sharing is unequal. In a polar covalent bond, sometimes simply called a polar bond, the distribution of electrons around the molecule is no … Sep 27, 2019 · A covalent bond is represented in the Lewis structure that shows electron sharing between atoms. Covalent bond and its types. A covalent bond which is additionally known as a molecular bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Covalent bonds are mostly formed between two non-metals. A coordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. In the formation of a simple or ordinary covalent bond, each atom supplies at least one electron to the formation of the bond – but that is not the case every time.
Nov 01, 2018 · Definition: covalent bond A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons A Dative covalent bond forms when the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond come from only one of the bonding atoms. A dative covalent bond is also called co-ordinate bonding. Common examples you should be able to draw that contain dative covalent bond (e.g. NH4 ... Coordinate covalent bond: Some times, during the formation of covalent bond, the shared pair is entirely contributed by only one atom This is called as coordinate covalent bond or dative bond. LEWIS DOT MODEL. To explain the formation of covalent bond, a simple qualitative model was developed by Gilbert Newton Lewis in 1916. According to this ... Once learners have mastered the skill of drawing electron configuration diagrams, they are ready to move on to bonding diagrams using the dot-and-cross method. This resource helps learners to visualise the position of atoms within simple molecules by experimenting with layouts and moving the tiles to complete the covalent bonds. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds.The bond may result from the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds.The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" …
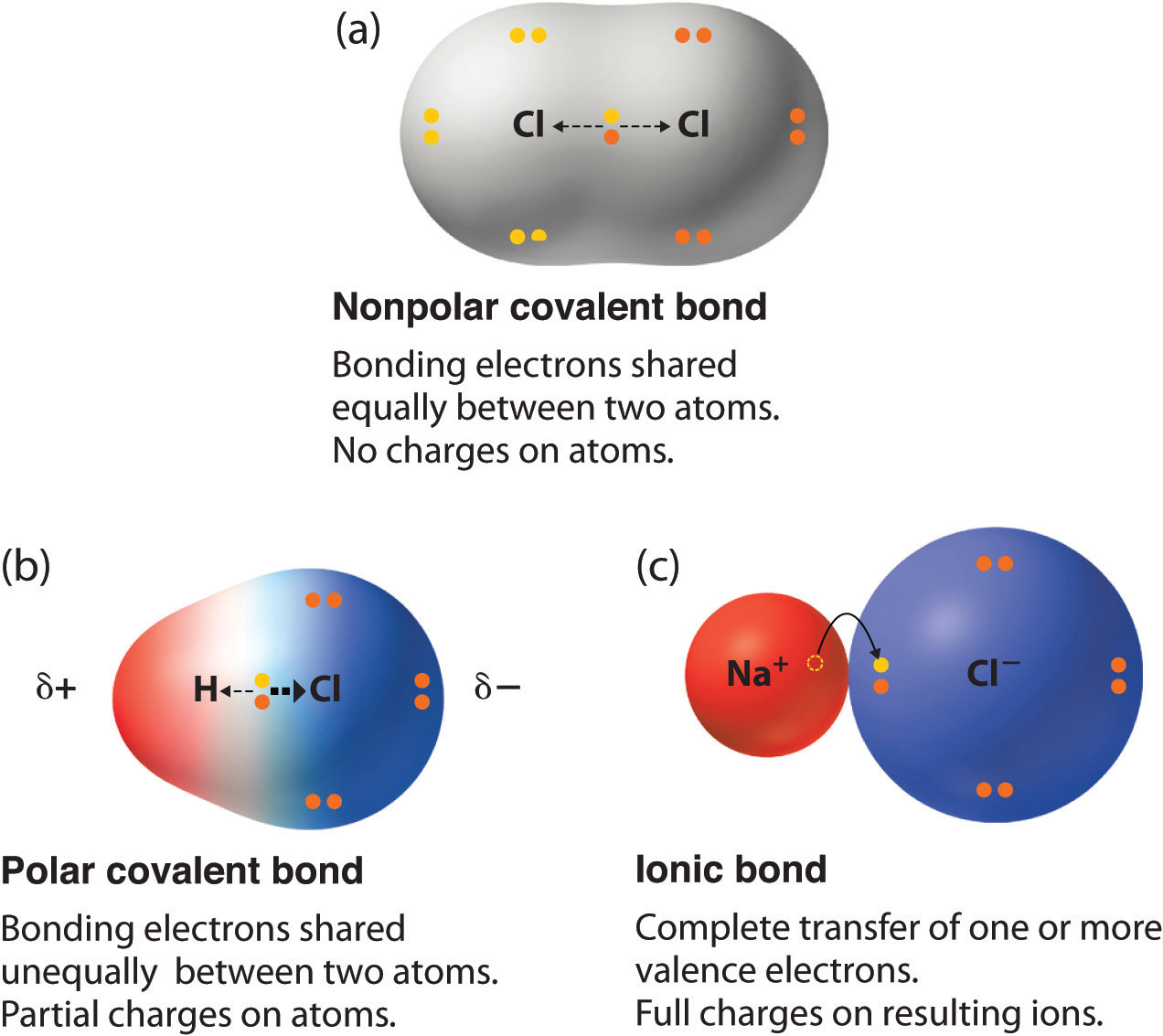
Pure vs. Polar Covalent Bonds. If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical, as in H 2, Cl 2, and other diatomic molecules, then the electrons in the bond must be shared equally.We refer to this as a pure covalent bond.Electrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus. Draw a diagram: Covalent bonds are shown in Lewis diagrams. In a Lewis diagram, dots represent unshared valence electrons and dashes represent pairs of shared electrons. Turn on Show Lewis diagram. What is the Lewis diagram for hydrogen, H 2? H - H. Form a bond: Now select Fluorine and create a molecule of fluorine, F 2. Take a snapshot of this ... Covalent Bonds • Although all covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons, they differ widely in the degree of sharing. • Covalent bonds can be divided into: - nonpolar covalent bonds and - polar covalent bonds. Difference in Electronegativity Between Bonded Atoms Type of Bond Less than 0.5 0.5 to 1.9 Greater than 1.9 Nonpolar covalent ... Dec 05, 2020 · A schematic diagram of a fluorescent nano-switch controlled by the dynamic covalent B-O bond between phenylboronic acid-functionalized carbon quantum dots and p-nitrophenol. Figure reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry (192).
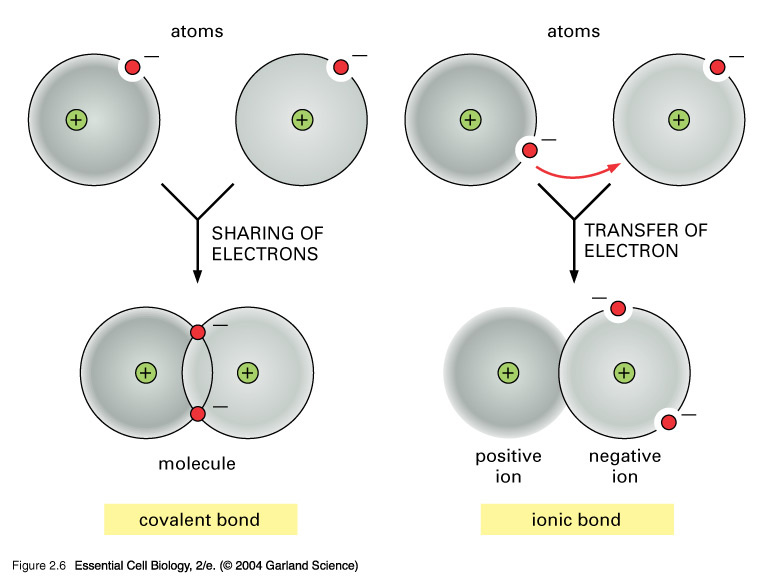
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond in which the atoms have different electronegativity values from each other. For example, sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) form an ionic bond to make NaCl (table salt). However, in a covalent bond, the atoms are bound to share electrons. For example, if we talk about water ( H2O), it is a polar covalent bond.
2. Lewis proposed that Covalent bonds consist of shared pairs of electrons. He created a powerful empirical formalism (Lewis dot structures) for understanding bonding in simple compounds. 3. Linus Pauling created a picture of covalent bonding that employed Quantum Mechanics (and won the 1954 Nobel Prize for it). The Covalent Bond
Draw a diagram: Covalent bonds are shown in Lewis diagrams. In a Lewis diagram, dots represent unshared valence electrons and dashes represent pairs of shared electrons. Turn on Show Lewis diagram. What is the Lewis diagram for hydrogen, H 2? H 4. Form a bond: Select Fluorine and turn on Highlight shared electrons. Create a molecule of fluorine ...
Covalent bonding is a form of chemical bonding between two non metallic atoms which is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms and other covalent bonds. Ionic bond, also known as electrovalent bond is a type of bond formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound.
Remember, covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons. Typically two, four, or six electrons are shared during covalent bonding. Covalent bonds are formed by nonmetals and some metalloids when they behave as nonmetals. Determine the number of valence electrons each element has, and click submit. You will then see the Lewis valence electron dot ...
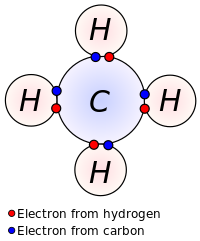
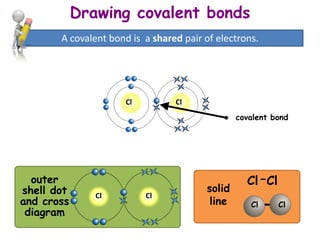
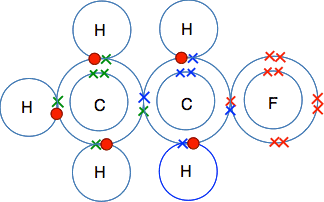
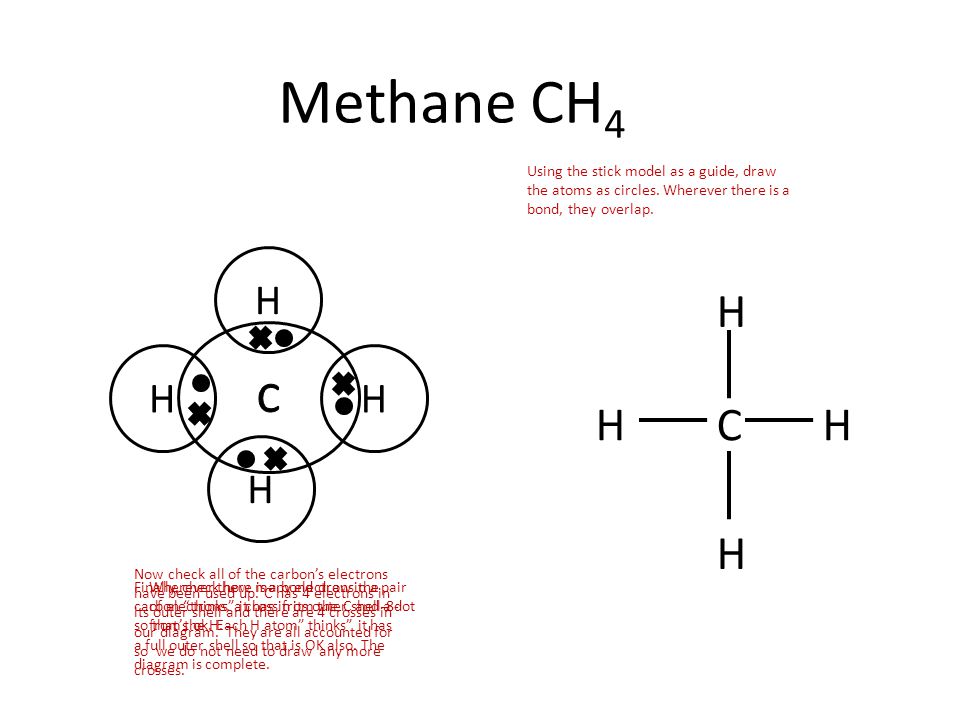
A dot and cross diagram can show the bonding in a small molecule: the outer shell of each atom is drawn as a circle circles overlap where there is a covalent bond electrons from one atom are drawn...
Oct 22, 2019 · A dative bond is also termed as Coordinate Covalent bond. it is that type of chemical bond in which one atom provides a shared pair of electron for the formation of a bond. OR. A chemical bond that is formed between two atoms due to sharing of the electron pair in which only one atom provides a shared pair of electron for bond formation.
A covalent bond forms when the difference between the electronegativities of two atoms is too small for an electron transfer to occur to form ions.Shared electrons located in the space between the two nuclei are called bonding electrons. The bonded pair is the "glue" that holds the atoms together in molecular units.
A Venn Diagram showing compare and contrast Covalent Bonds and Ionic Bonds. You can edit this Venn Diagram using Creately diagramming tool and include. DO NOW - 2/10/10 Create a Venn Diagram of Covalent Bonds versus Ionic Bonds 3 items in each space, write a 4 sentence summary Turn in at the end of class.
A covalent bond forms when the difference between the electronegativities of two atoms is too small for an electron transfer to occur to form ions. Shared electrons located in the space between the two nuclei are called bonding electrons. The bonded pair is the "glue" that holds the atoms together in molecular units.
Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity When a chemical bond is formed, the electrons feel their environment. If the bond formation dealt between Na and Cl, due to Na's low ionization energy and Cl's high electron affinity, Cl grabs an electron from Na's valence shell to form Cl-ion and Na becomes Na +.In this case, the bonding is ionic.In the case of two carbon atoms, the resulting chemical ...
The bond between the C and O atoms is a double bond A covalent bond composed of two pairs of bonding electrons. and represents two bonding pairs of electrons between the atoms. If using the rules for drawing Lewis electron dot diagrams don't work as written, a double bond may be required.
Dot and cross diagrams for covalent bonding **HIGHER TIER: Any reference to H2O, NH3, CH4, O2, N2 or CO2 bonding is higher tier.** We can use dot and cross diagrams to show how a pair of electrons...
The covalent bond thus develops a partial ionic character. Such a covalent bond is referred to as a polar covalent bond or partially ionic covalent bond the molecules possessing such bonds are known as polar covalent molecules or simply polar molecules. For example, HF is a polar molecule.
Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metallic atoms characterized by the sharing of electron pairs between the atoms and other covalent bonds with electronegativity difference is greater than 2.0 (<2.0). In the case of covalent bond formation, polyatomic ions are formed.
Covalent Bond venn diagram shows the similarities and differences between the chemical bonds. Click on the diagram to edit online and .Although these bonds are weaker than the internal ionic or covalent bonds existing between the atoms within molecules, the accumulated strength of hydrogen bonds within living organisms is highly significant and ...
As covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons between atoms, we draw overlapping circles to show the overlapping of the electron shells, and draw in pairs of dots and crosses to show the sharing of electrons. Covalent molecules examples. Let's look at how to illustrate the covalent bonds using dot- and- cross diagrams.
The bond dipole moment uses the idea of electric dipole moment to measure the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule.It occurs whenever there is a separation of positive and negative charges. The bond dipole μ is given by: =. The bond dipole is modeled as δ + — δ – with a distance d between the partial charges δ + and δ –.It is a vector, parallel to the bond axis, …
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. [better source needed] For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the ...
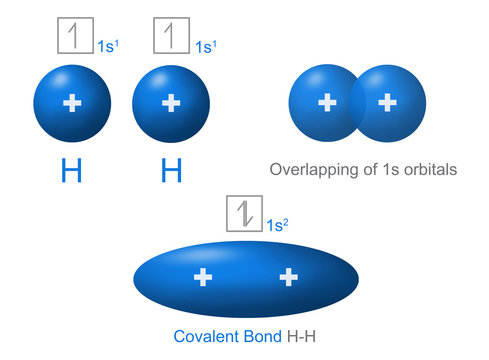
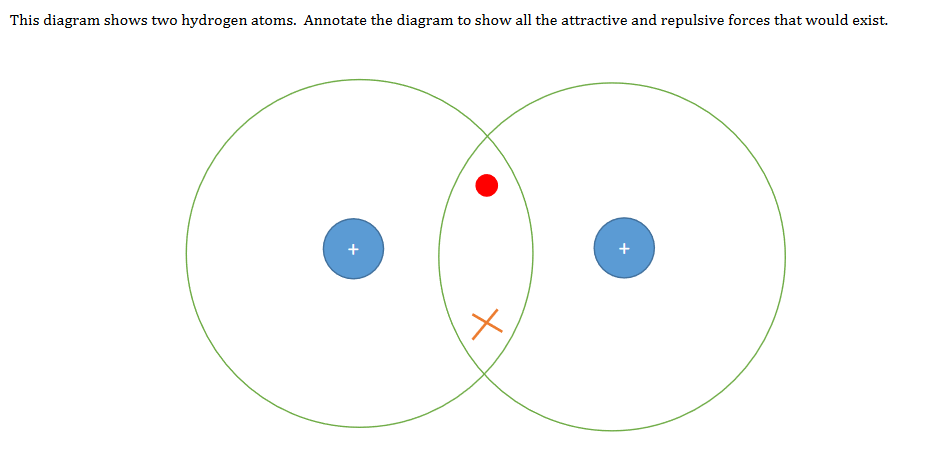
an electron with the other, forming a covalent bond. In H 2, each H atom has 2 electrons. each H has 1 e-and wants 1 more shared pairs can be represented as lines between atoms a hydrogen molecule (diatomic = 2 atoms) H + H H H H H H 2 H's share e-'s forming a covalent bond. . .. Here’s another example, this time for chlorine.
When these bonding orbitals are occupied by a pair of electrons, a covalent bond, the sigma bond results. Although we have ignored the remaining p-orbitals, their inclusion in a molecular orbital treatment does not lead to any additional bonding, as may be shown by activating the fluorine correlation diagram below.
A covalent bond that has an equal sharing of electrons and the electronegativity difference is zero is called a nonpolar covalent bond. Polar Covalent Bond When the electrons spend more time around the more non-metallic atom, the sharing of the electron pair becomes unequal and results in the formation of polar covalent bonds.
Covalent Bonding in H2 H. .H Two hydrogen atoms, each with 1 electron, can share those electrons in a covalent bond. H:H •Sharing the electron pair gives each hydrogen an electron configuration analogous to helium.
4. Fulfill all atoms octet by making a covalent bond. In this step, we will use a covalent bond to fulfill the octet of atoms if necessary. As in the 3rd step structure, Carbon not getting what it needs, so, simply convert the lone pair on nitrogen to a covalent bond.
Each dot structure covalent lewis bonds lewis dot diagram. Some of the worksheets for this concept are lewis dot structures and molecule geometries work covalent bonding work bonding basics chapter 7 practice work covalent bonds and molecular covalent ws lewis structures covalent practice problems h s so ch br hcn.
A covalent bond can be represented by a straight line or dot-and-cross diagram. Water formula is presented in diagram covalent bond takes place between two hydrogen. Covalent bonds are directional where the atoms that are bonded showcase specific orientations relative to one another.





















Komentar
Posting Komentar