40 reaction coordinate diagram rate determining step
Answered: Determine the EA for the… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text:Determine the EA for the rate-determining step (step 1) for this reaction coordinate diagram, in kJ. 100 87 kJ. 80 78 kJ PE (kJ) 60 55 kJ 50 kJ Created by E. Lee for Virtual Virginia (20 40 20 20 kJ Reaction Progress Expert Solution Want to see the full answer? Check out a sample Q&A here See Solution star_border Endothermic Reaction Coordinate Diagram - schematron.org A typical reaction coordinate diagram for a mechanism with a single step is shown below: Below is a reaction coordinate diagram for an endothermic reaction. The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the.
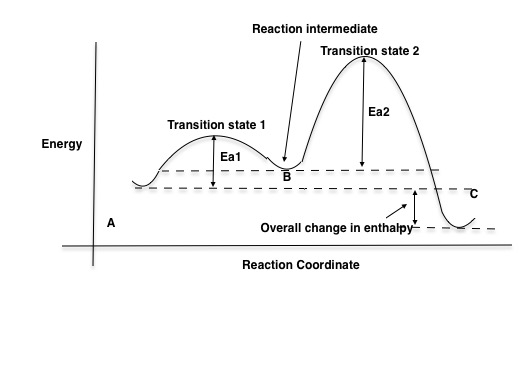
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry - Rate determing ... step Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Ratedetermining step (rds; ratelimiting step): The mechanismstep with the greatest activation energy(i.e., the slowest step) and therefore the step that has the greatest influence on reaction rate. Eact(step 2) > Eact(step 1) so rate(step 2) < rate(step 1). step.

Reaction coordinate diagram rate determining step
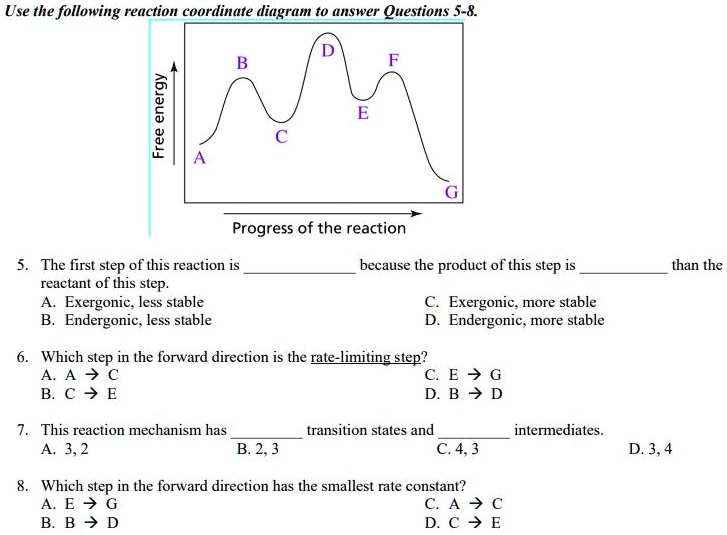
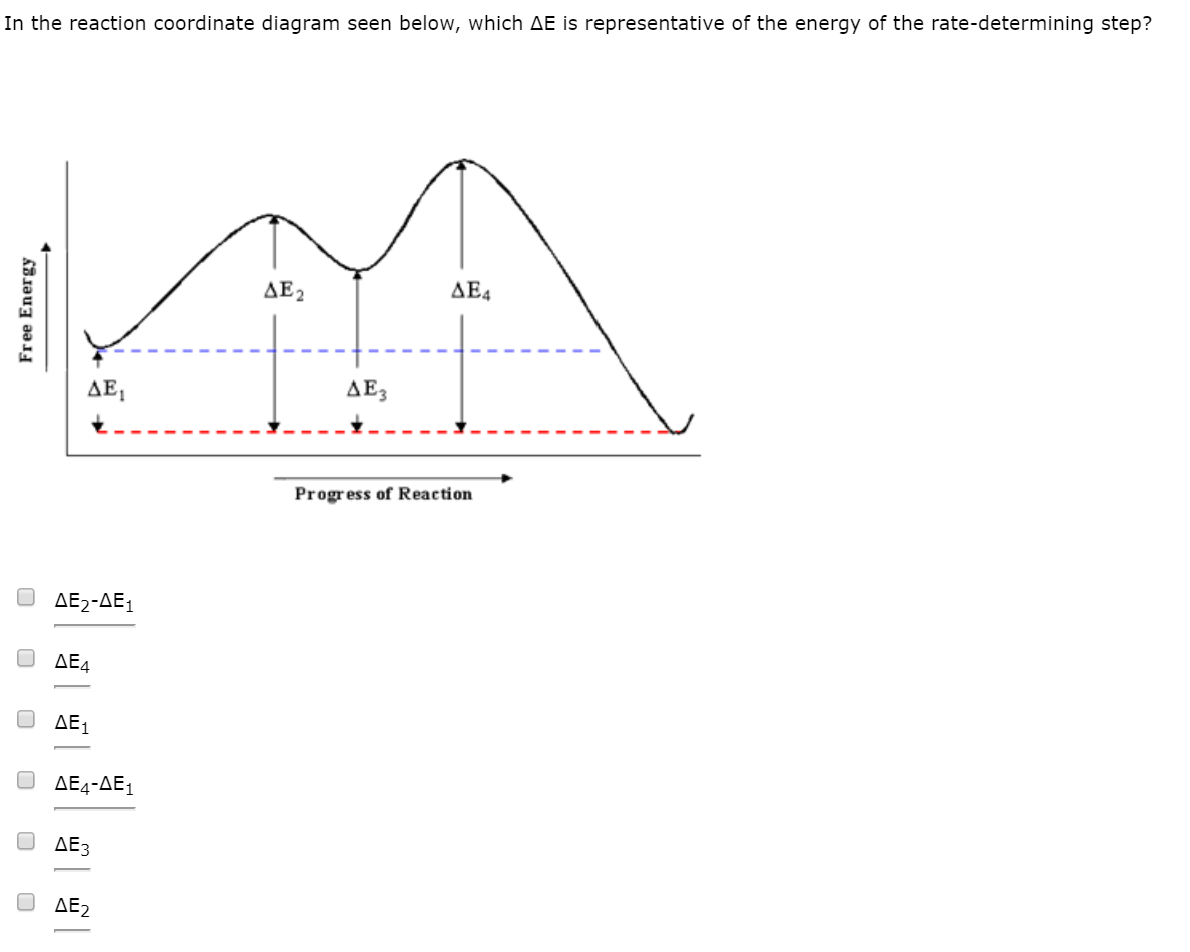
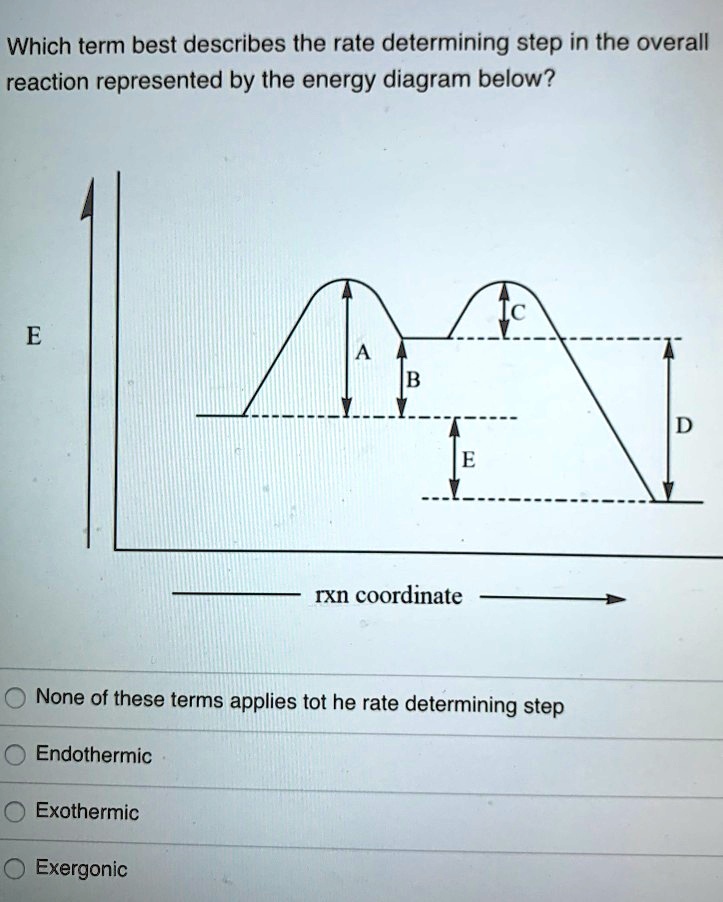
Answered: 23. Consider the reaction coordinate… | bartleby Consider the reaction coordinate… | bartleby. 23. Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown. What is the rate-determining step in the conversion of A to G? D B F E A G Progress of rxn Free Energy. Reaction Coordinates and Mechanism - Chemistry 302 Reaction mechanisms also have "fast" and "slow" steps. We can always identify the "rate limiting step" as it should have the largest barrier. In the picture above the first step would be the rate limiting step since it has the highest barrier. Writing out this mechanism we would have Step 1 A → B slow Step 2 B → C fast Step 3 C → D fast 6.3: A Quick Review of Thermodynamics and Kinetics ... The reaction of a weak acid such as acetic acid with a weak base such as water, on the other hand, is unfavorable and has an equilibrium constant that is a very small (much less than 1) positive number: we can visualize this in a reaction coordinate diagram as an 'uphill' reaction, in which \(\ce{\Delta G^{\circ}_{rnx}}\) is positive.
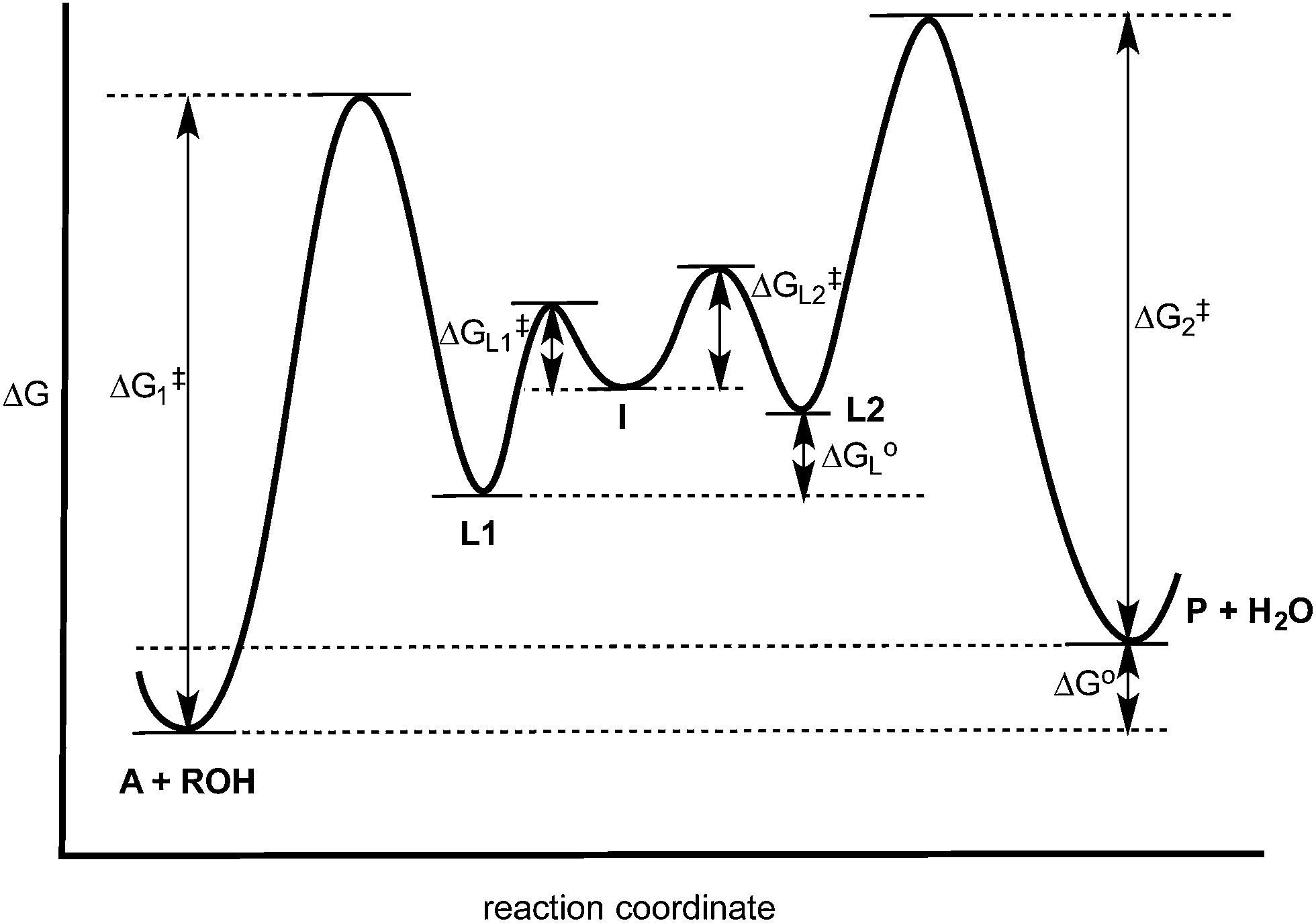
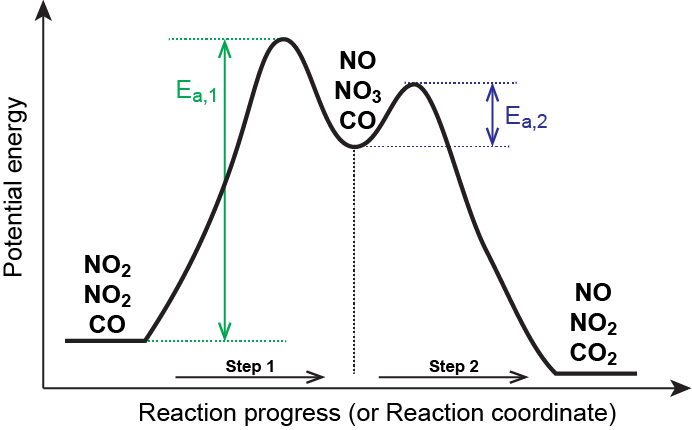
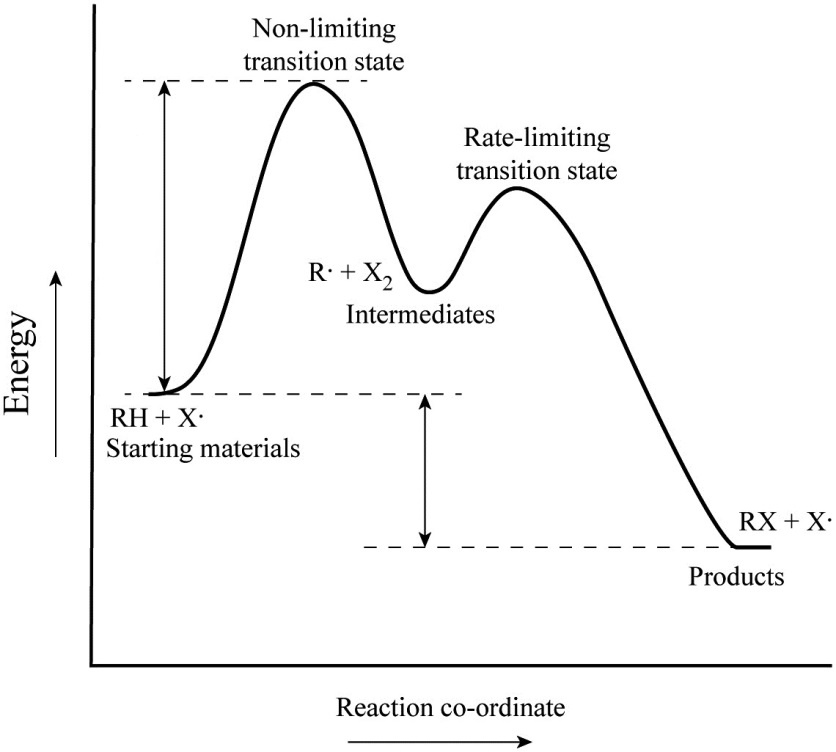
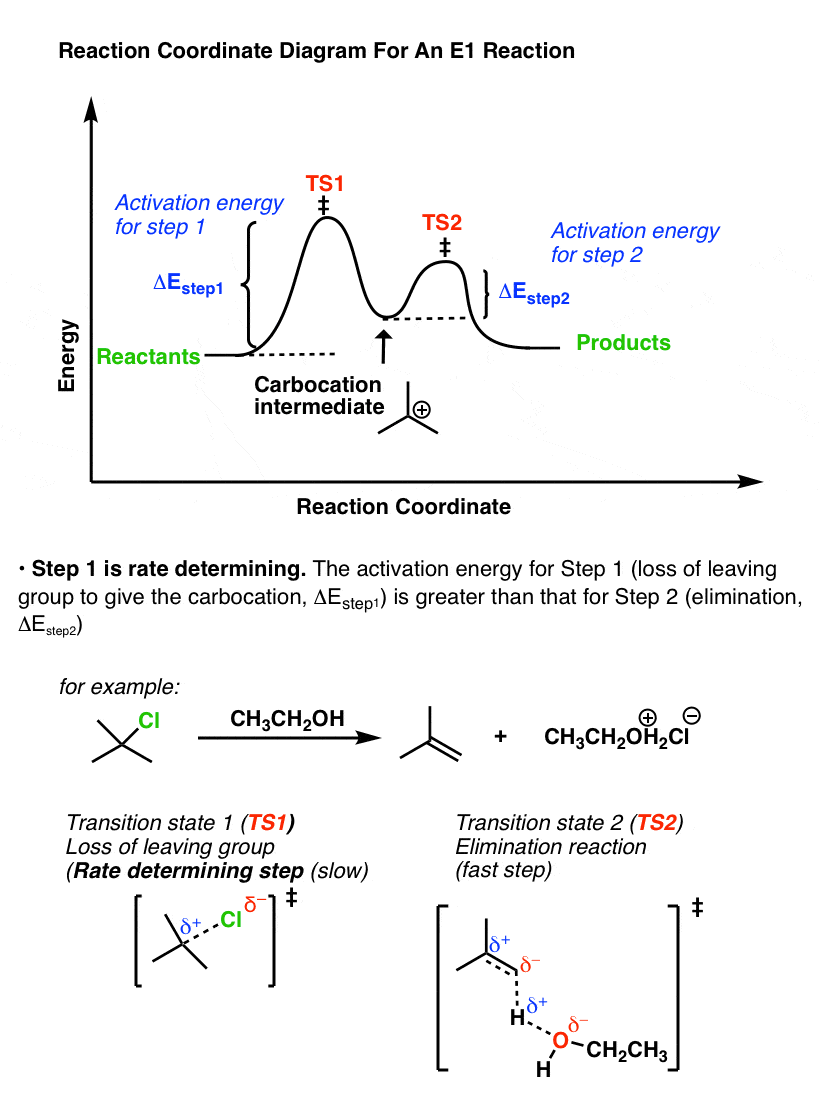
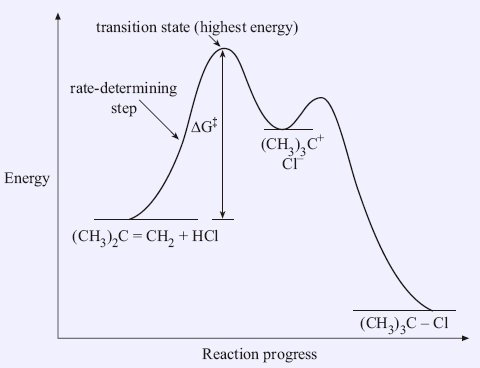
Reaction coordinate diagram rate determining step. Rate-determining step - Wikipedia First step rate-determining In fact, however, the observed reaction rate is second-order in NO 2 and zero-order in CO, with rate equation r = k [ NO 2 ] 2. This suggests that the rate is determined by a step in which two NO 2 molecules react, with the CO molecule entering at another, faster, step. Answered: 80 20 5 Determine the EA for the… | bartleby 80 20 5 Determine the EA for the rate-determining step (step 1) for this reaction coordinate diagram, in kJ. 87.kJ. 78 kJ PE (kJ) 09 55KJ 50KJ 20 kJ Reaction Progress Created by E. Lee for Virtual Virginia (2021) IIO V 24 ) 8. 6. PDF Elimination Reactions - University of Minnesota a rate determining E - step reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a common intermediate) (as base) CH3OH Ratio of E1/SN1 products depends on the relative basicity/ l hili it f th Br _ nucleophilicity of the electron donor. (as nucleophile) Nucleophilicity and basicity are often correlated. Energy profile (chemistry) - Wikipedia S N 1: Figure 10 shows the rate determining step for an S N 1 mechanism, formation of the carbocation intermediate, and the corresponding reaction coordinate diagram. For an S N 1 mechanism the transition state structure shows a partial charge density relative to the neutral ground state structure.
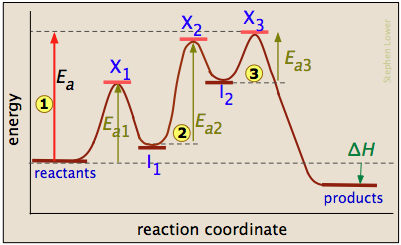
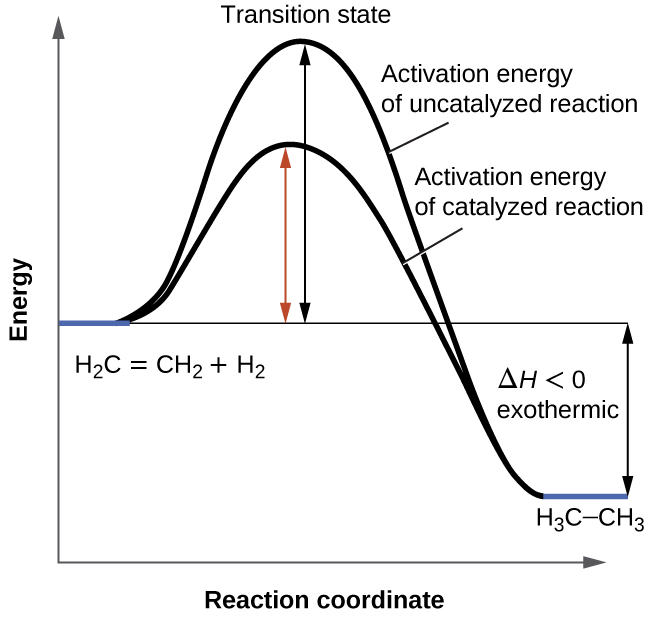
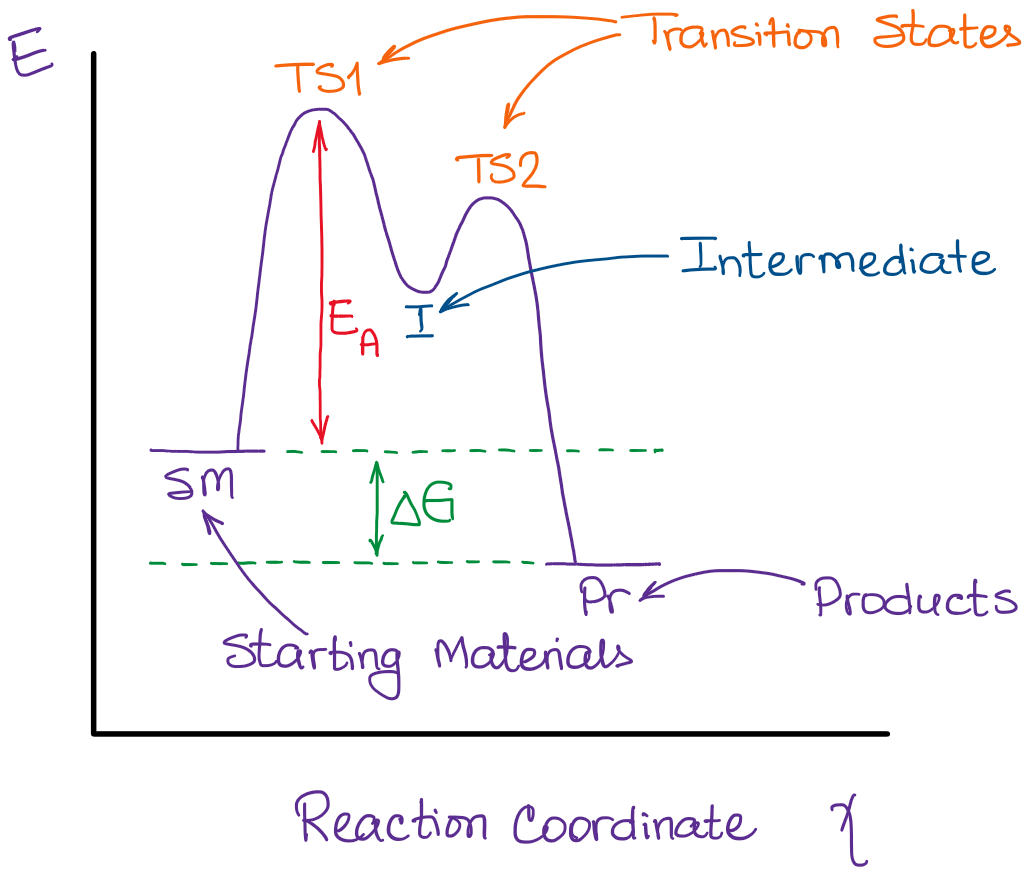
PDF Potential Energy vs Reaction Progress (Coordinate) Diagram Sketch a potential energy vs reaction progress (coordinate) diagram for a catalyzed two-step endothermic reaction in which the second step is rate determining (RDS). On your sketch, label the position of reactants, products, any intermediates, any activated complexes (transition states), activation energy for the RDS and ∆H for the first step ... Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - University of Illinois ... The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram. Rate Determining Step for Reaction Coordinate Diagram ... The takeaway is that high transition state = rate determining step = slowest step in a RCD that you could actually draw. 0 D daftpatton New Member 10+ Year Member Joined Jan 17, 2011 Messages 4 Reaction score 0 May 7, 2011 #8 Graffiti said: Let's say you're looking at a reaction coordinate diagram for an exothermic reaction. Review of Reaction Kinetics: Review Test - SparkNotes 37. In a multi-step reaction, how can you tell from the reaction coordinate diagram what the rate determining step is? The step with the highest activation energy The step whose transition state has the highest energy The step with the most stable intermediate product The step with the least stable intermediate product
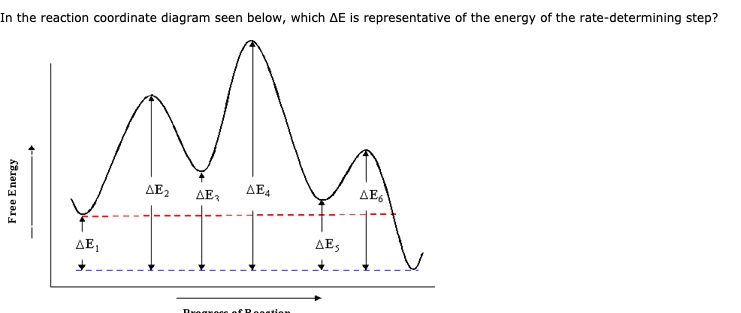
16.1 Rate-determining step (HL) - YouTube Understandings:Reactions may occur by more than one step and the slowest step determines the rate of reaction (rate determining step/RDS). Reaction Coordinate - Chemistry 302 For example, in the reaction of CH 3 Cl + OH- to form CH 3 OH and Cl-, the mechanism of this reaction is a single step in which the CH 3 Cl collides with the OH- and forms the products. We can envision a reaction coordinate for this reaction which is the lengthening of the C-Cl bond (the one that is breaking) and the shortening of the C-O bond ... kinetics - Which step below is rate determining ... Given a reaction coordinate (energy diagram), the rate determining step can be determined by taking the largest energy difference between any starting material or intermediate on the diagram and any transition state that comes after it. That transition state will then be the rate-determining step of a given reaction. CHEM 2461 Flashcards | Quizlet The energy of the reactants vs the products on the reaction coordinate diagram can be used to identify the change in _____ during the reaction . kinetics ... The _____ of the alkyl halide to give a _____ is the rate-determining step of an Sn1 reaction. Sn1 (Sn1 or Sn2) unimolecular rate. Sn1 (Sn1 or Sn2) have a carbocation intermediate ...
reaction coordinate, kinetics, equilibrium in example ... By the diagram, rate determining step of forward reaction is the first one (because activation energy is the highest and let's say it is one and only factor for RDS in this case). so Vf=k1 [A] [B]. RDS in reverse reaction is second step of the reaction judging by the diagram activation energy (M->A+B). So I used pre-equilibrium approximation ...
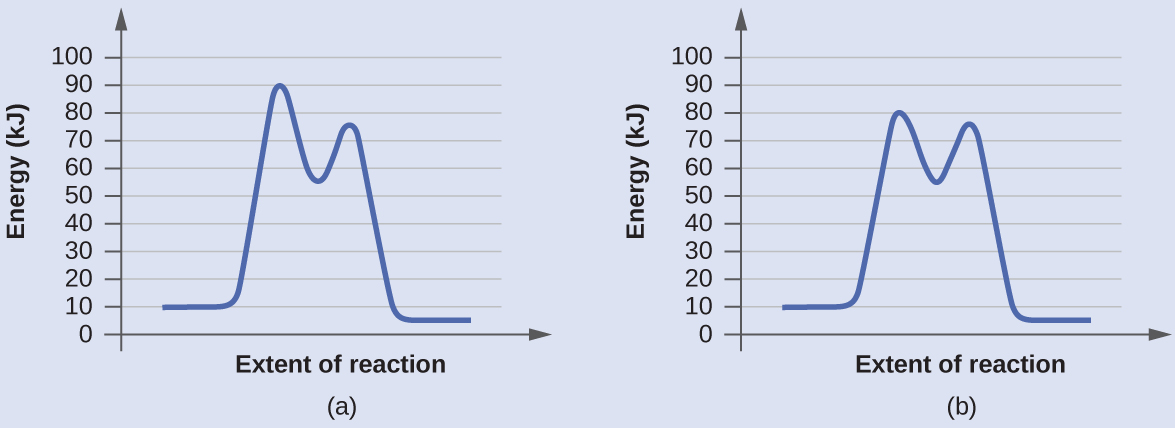
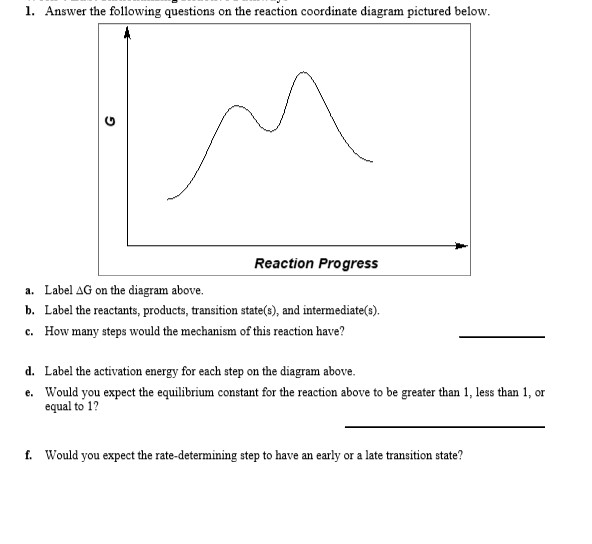
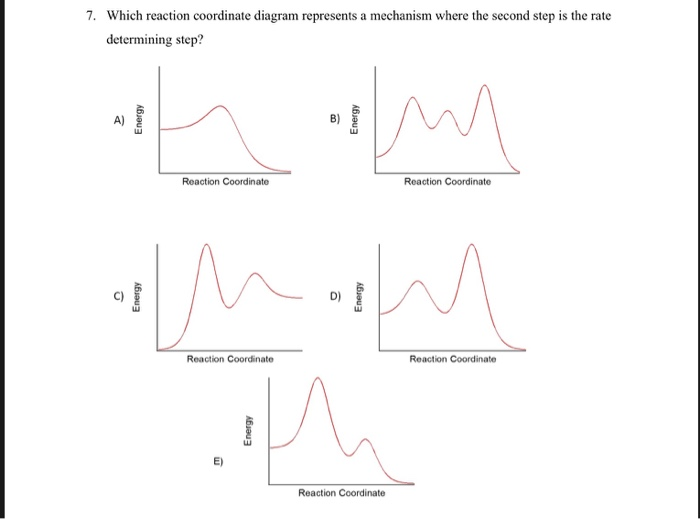
PDF Additional Problems for practice: 1. Draw a reaction ... 1. Draw a reaction energy diagram (graph of potential energy versus reaction coordinate) for a three-step endothermic reaction with the (a) first step rate-determining (b) the second step rate-determining (c) the third step rate determining Do the same (a-c) for a three step exothermic reaction. For each graph,
Arrhenius Theory and Reaction Coordinates We can always identify the "rate limiting step" as it should have the largest barrier. In the picture above the first step would be the rate limiting step since it has the highest barrier. Writing out this mechanism we would have Step 1 A → B slow Step 2 B → C fast Step 3 C → D fast © 2013 mccord/vandenbout/labrake scroll to top
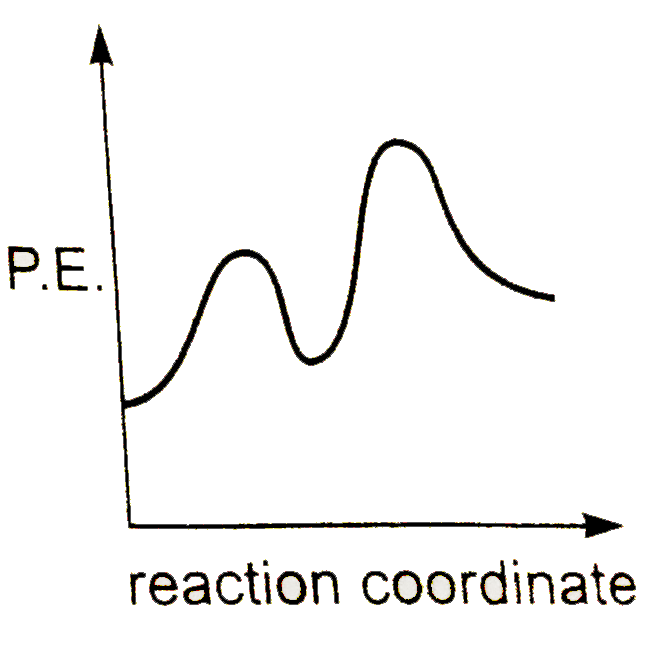
How do you find the rate determining step from a graph ... The rate determining step in a reaction mechanism is the slowest step. It is characterized by its high activation energy. Consider the energy diagram represented below of a two-step mechanism. The first step is the slow step since it has the highest activation energy. Here is more about this topic in the following video:
3.2.3: Rate Determining Step - Chemistry LibreTexts Rate determining step is the slowest step within a chemical reaction. The slowest step determines the rate of chemical reaction.The slowest step of a chemical reaction can be determined by setting up a reaction mechanisms. Many reactions do not occur in a single reaction but they happen in multiple elementary steps. Consider this reaction:
Ch 8 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science This implies that the rate determining step involves an interaction between two species, the nucleophile and the organic substrate. This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group.
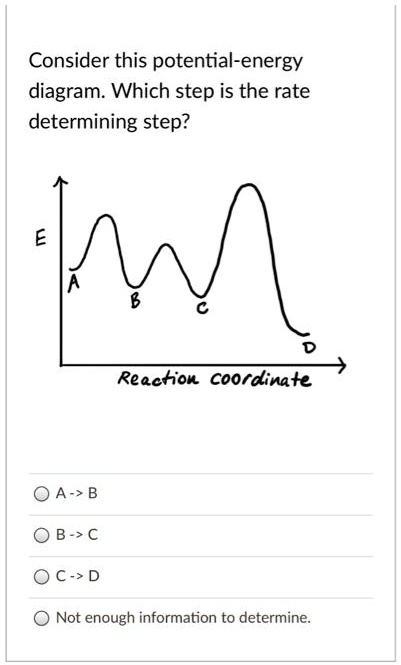
Solved Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown ... Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown. What is the rate-determining step in the conversion of A to G? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 95% (19 ratings)
6. Reaction Coordinate Diagram - VIZISCIENCE® INTERACTIVE LABS 6. Reaction Coordinate Diagram Given the following reaction, sketch a reaction coordinate graph. The reaction involves two steps, step 1 is the slowest step and step 2 is the fastest step. Both steps are exothermic. Indicate on the diagram the overall enthalpy change of the reaction, the reaction for the transition states and intermediate states.
6.6: Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - Chemistry LibreTexts rate = k [reactant 1] [reactant 2] . . . which tells us that the rate of the reaction depends on the rate constant k as well as on the concentration of both reactants. The rate constant can be determined experimentally by measuring the rate of the reaction with different starting reactant concentrations.
6.3: A Quick Review of Thermodynamics and Kinetics ... The reaction of a weak acid such as acetic acid with a weak base such as water, on the other hand, is unfavorable and has an equilibrium constant that is a very small (much less than 1) positive number: we can visualize this in a reaction coordinate diagram as an 'uphill' reaction, in which \(\ce{\Delta G^{\circ}_{rnx}}\) is positive.
Reaction Coordinates and Mechanism - Chemistry 302 Reaction mechanisms also have "fast" and "slow" steps. We can always identify the "rate limiting step" as it should have the largest barrier. In the picture above the first step would be the rate limiting step since it has the highest barrier. Writing out this mechanism we would have Step 1 A → B slow Step 2 B → C fast Step 3 C → D fast
Answered: 23. Consider the reaction coordinate… | bartleby Consider the reaction coordinate… | bartleby. 23. Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown. What is the rate-determining step in the conversion of A to G? D B F E A G Progress of rxn Free Energy.















Komentar
Posting Komentar