42 saving investment diagram
Savings vs Investment - Utah Education Network Option 2: Savings vs Investing Use the Savings vs Investment Lecture Notes (pdf) and the Saving and Investment Transparency (pdf) to have a class discussion. To explain liquidity, you can use three cups, one filled with water, the other filled with water that has been frozen and one empty. 23.4 The National Saving and Investment Identity ... A country's national savings is the total of its domestic savings by household and companies (private savings) as well as the government (public savings). If a country is running a trade deficit, it means money from abroad is entering the country and is considered part of the supply of financial capital.
PDF Name Date SAVING VS INVESTING VENN DIAGRAM Name ________________________________ Date ________ SAVING VS INVESTING VENN DIAGRAM Directions: Fill in the Venn Diagram. Provide unique characteristics of Saving and Investing in each individual circle. In the area where the circles overlap, list characteristics that are shared by both investing and saving. SAVING INVESTING FINANCE

Saving investment diagram
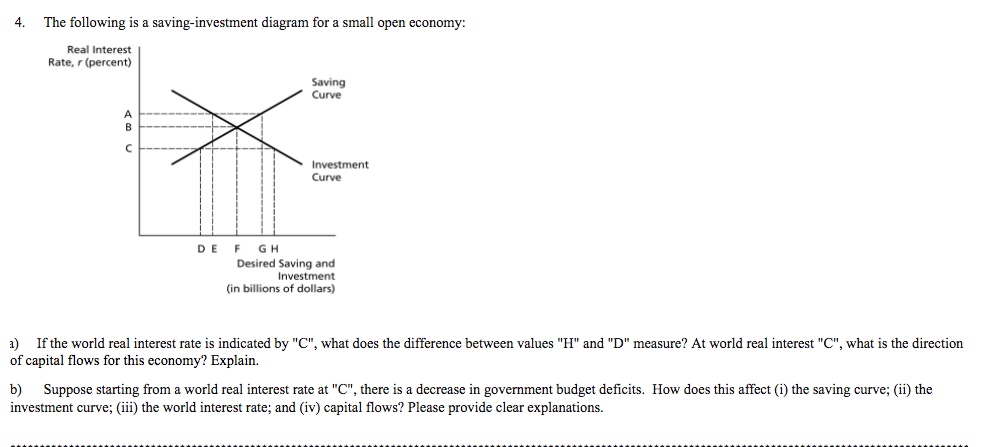
(d) Use the Saving-Investment diagram for a | Chegg.com Question: (d) Use the Saving-Investment diagram for a manufacturing based economy to analyze the effect on the real interest rate and quantity of savings and investment when (i) the government budget surplus increases and (ii) there is an improvement in technology in the manufacturing sector. Analyze each incident separately. (6 marks) (PDF) saving investment practice | jingjing ma - Academia.edu Use the saving and investment identities from the National Income Accounts to answer the following questions. Suppose the following values are from the national income accounts of a country with a closed economy. (All values are in billions.) Y = $600 T = $100 C = $400 G = $120 a. In the saving investment diagram an increase in current ... 10) In the saving—investment diagram, an increase in current output would A) shift the saving curve to the left. B) shift the investment demand curve to the left. C) not shift the curves. D) shift the saving curve to the right. Answer: D
Saving investment diagram. Saving vs. Investing Venn Diagram by Twin Business ... Saving vs. Investing Venn Diagram This download is a Venn diagram/circle map that students can use to compare the differences and similarities between saving and investing. Many students believe they are the same thing but after this activity they will realize there is many differences. Chapter 4 Flashcards - Quizlet 49. The saving-investment diagram shows that a higher real interest rate due to a leftward shift of the saving curve (a) raises the profitability of investment for firms. (b) causes the amount of firms' investment to increase. (c) increases the total amount of saving because of the increase in the real interest rate. The Relationship between Saving and Investment (Explained ... Modern economists use the concepts of saving and investment in two different senses. In one sense, saving and investment are always equal, equilibrium or no equilibrium. In the second sense, saving and investment are equal only in equilibrium; they are unequal under conditions of disequilibrium. Solved Explain why the saving curve slopes upward in the ... Explain why the saving curve slopes upward in the saving-investment diagram O A. Higher interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of future consumption activity. OB. Higher interest rates provide an incentive for individuals to consume more in the present and future. O c. Higher interest rates lead to increased government purchases. OD.
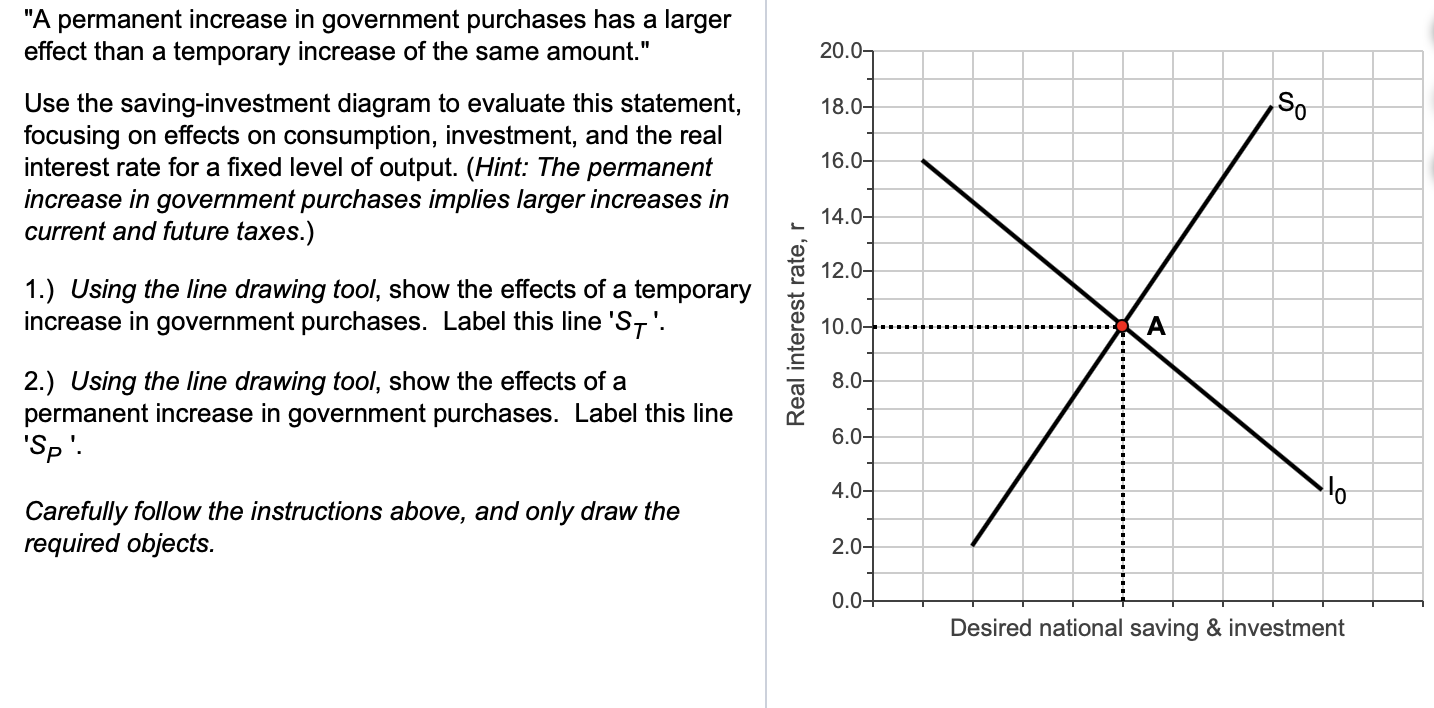
10 Money-Savings Charts To Save More Money | Clever Girl ... If you want to save faster than the 52-week chart, then the 26-week money-saving chart is for you. You will save $1,378 in six months rather than a year. This chart lists weeks 1-26 and the amount for each week. Rather than only adding an additional dollar to each week, you will add an additional $4 every week until you reach 26 weeks. Macro Chapter 4 Flashcards - Quizlet The saving-investment diagram shows that a higher real interest rate due to a leftward shift of the saving curve. causes the total amounts of saving and investment to fall. for a household with a given level of income, how are consumption and saving linked? Saving= Income - consumption. Saving and Investment: Paradox of Thrift (With Diagram) This is demonstrated in Fig. 3.13 where S 1 S 1 is the initial saving curve. l p is the planned induced investment line. Thus, investment is no longer assumed here as an autonomous one. It is dependent on income. S 1 S 1 and I p curves intersect each other at point E 1. Answered: 1. Use a saving-investment diagram to… | bartleby 1. Use a saving-investment diagram to explain what hap- pens to saving, investment, and the real interest rate in each of the following scenarios in a closed economy. ja. Current output rises due to a temporary produc- tivity increase. Vb.
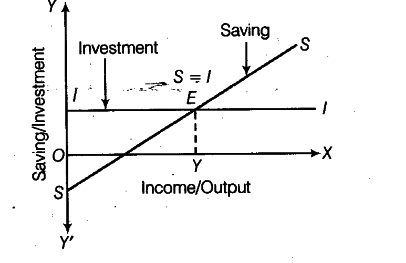
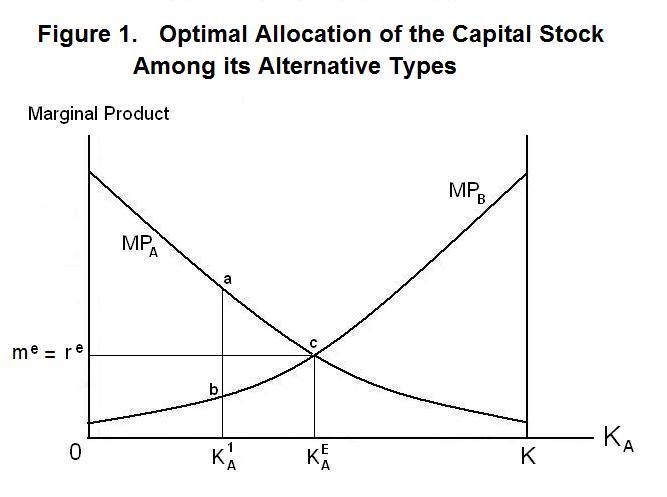
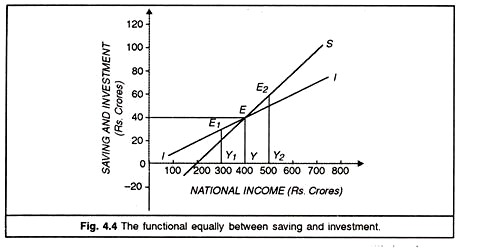
Saving and Investment Equality (With Explanation and Diagram) This is known as the functional equality of saving and investment and this is shown in the table and diagram as follows. We have shown the figures of the table given above in the diagram 4.4. National disposable income is shown on the X-axis. The saving schedule is SS. The investment schedule is II. PDF Topic 1 : Saving and Investment - University of Oxford 1.1 "The equality of saving and investment is a na- tional income accounting identity." Imagine we have and economy that produces and capital good K and a consumption good C. Its production function is defined as follows. F(K,L) = Y (1) where Y is a (K,C) bundle, and L is the labor supply. Saving vs. Investing Money - The Balance Saving money and investing money are entirely different things, with different purposes and different roles in your financial strategy. Saving money involves setting funds aside in safe, liquid accounts. Investing involves buying an asset like stocks in hopes of earning a return. Make sure you are clear on this fundamental concept before you ... Use a saving investment diagram to explain what happens to ... 80) Use a saving - investment diagram to explain what happens to saving, investment, and the real interest rate in each of the following scenarios in a closed economy. (a) Current output rises due to a temporary productivity increase.
EC2102 - Tutorial 2 Savings, Investment and the Interest ... The below is an interactive graph of savings and investment. For simplicity, we will use the previous assumption that saving is fixed (i.e. does not depend on the interest rate). This results in a vertical savings line as regardless of the interest rate there will be no change in the quantity saved.
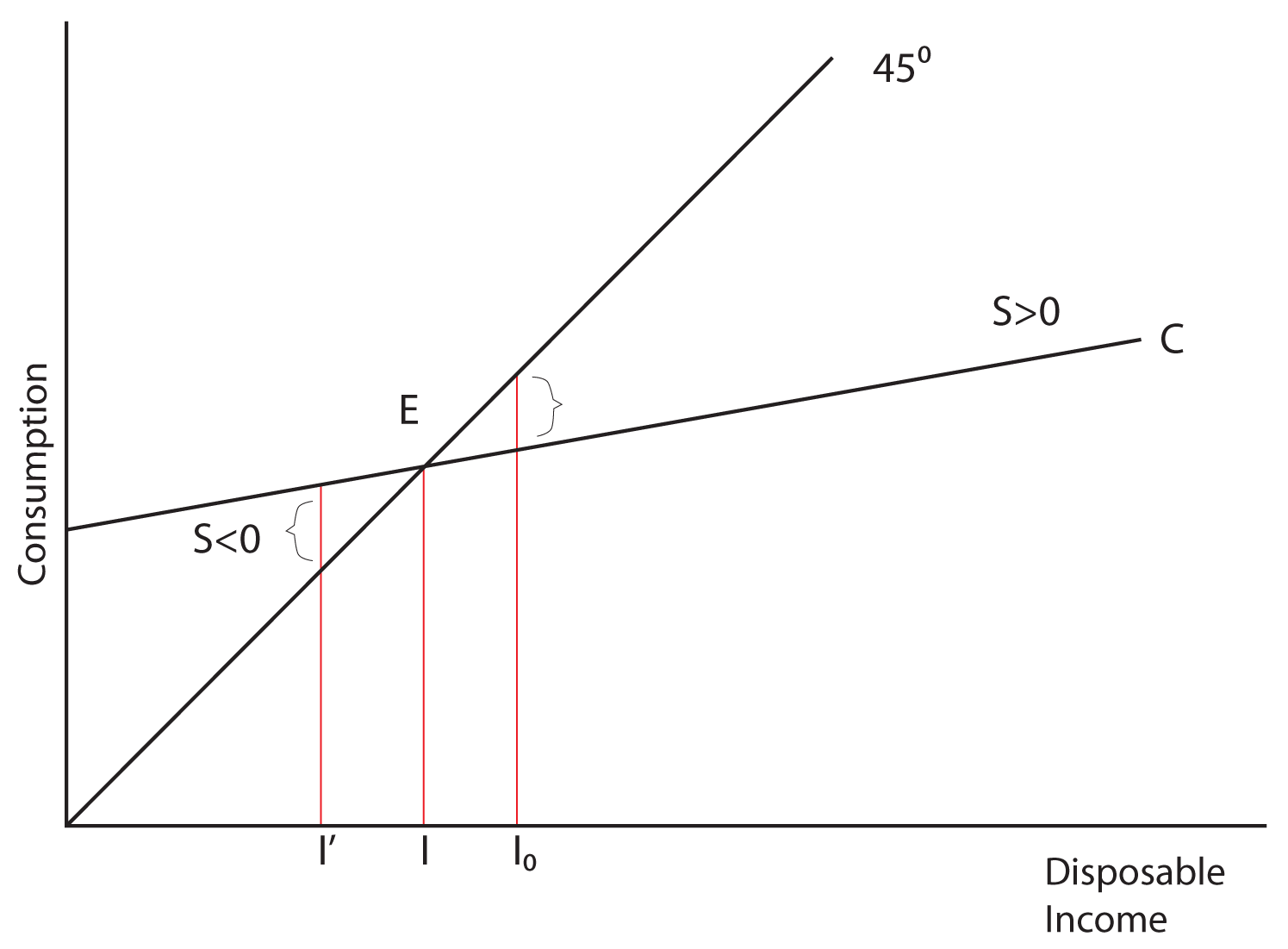
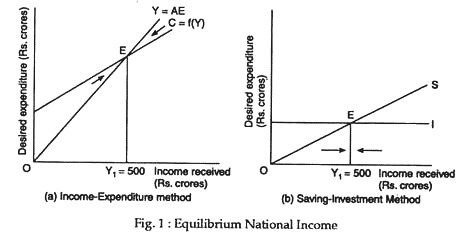
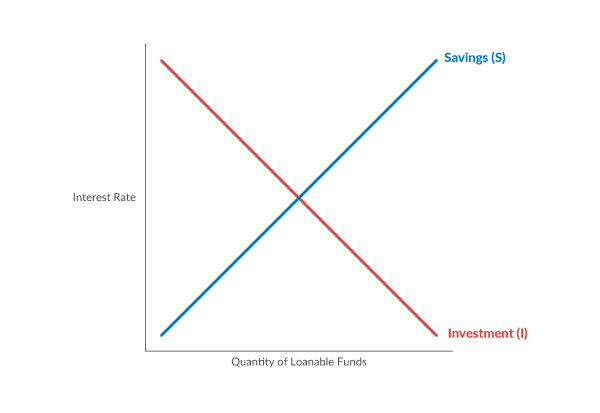
The Saving-Investment Approach: Determination of National ... In the lower part of this diagram we have draw intended savings curve SS and intended investment curve II. It is worthwhile to note that saving curve SS has been derived from the consumption function curve C and measures the gap between income and consumption at various levels of income.
Lecture 5: Saving and Investment - Kent State University Saving is, after all income minus taxes minus consumption. Thus S = Y - T - C. That is, Saving = Income lessTaxes lessConsumption Motives for Saving People save so that they can consume more in the future. A decision to spend now or save is really a choice of when to spend - now or in the future. The decision depends on
Saving vs. Investing Venn Diagram | Venn diagram, Holiday ... Description Saving vs. Investing Venn Diagram This download is a Venn diagram/circle map that students can use to compare the differences and similarities between saving and investing. Many students believe they are the same thing but after this activity they will realize there is many differences. An answer key is provided for you.
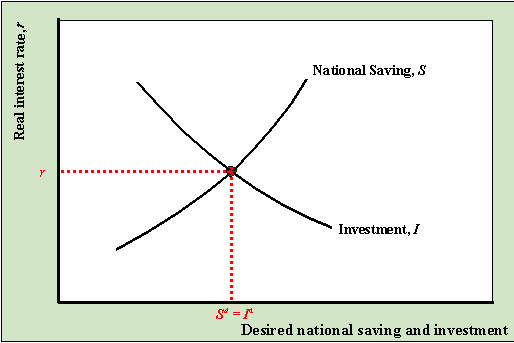
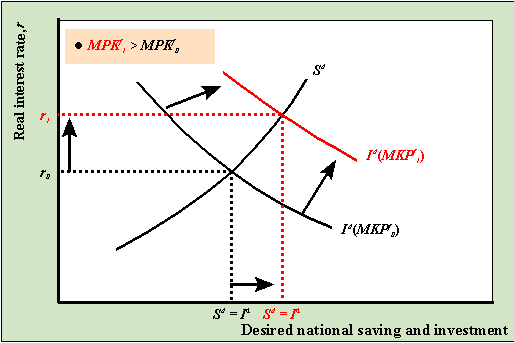
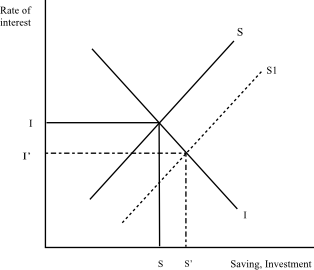
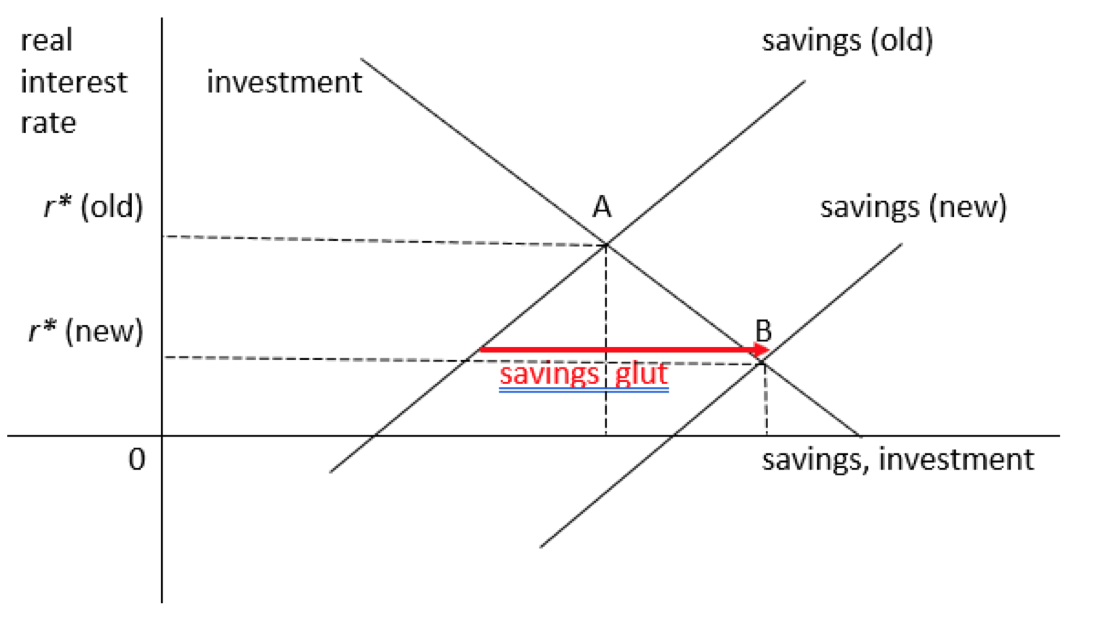
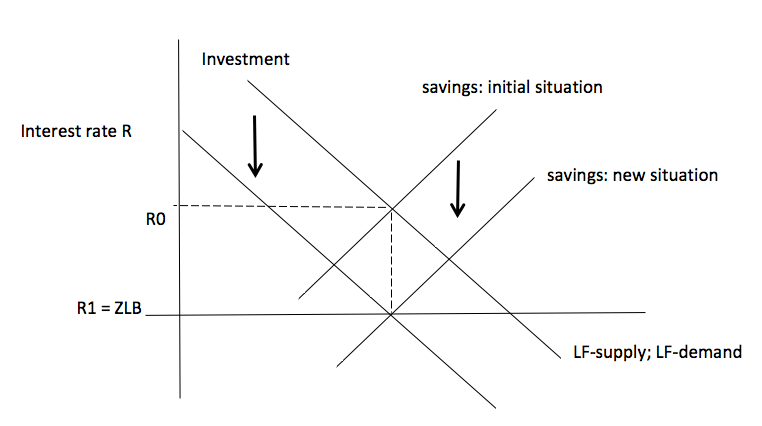
goods market equilibrium - University of Washington The diagram below illustrates a situation where the real interest rate is higher than the equilibrium interest rate. At r 0 > r*, the return to saving is high but the cost of investment is high so that desired saving is greater than desired investment: there is an excess supply of saving. In this case, banks have more cash on hand than they can ...
PDF The Pros and Cons of Saving and Investing 8. On the board, draw two Venn diagrams, one representing saving and the other representing investing. For each Venn diagram, the left represents pros, the right represents cons, and the middle represents the overlap between pros and cons. Have students work in small groups to identify three to five additional pros or cons of savings accounts.
Macnotes4 - Rutgers University We can graph savings and investment like a supply and demand graph. Investment is the demand component, and savings is the supply componenet. The intersection of S(r) and I(r) determines the equilibrium real rate of interest. Then, if interest rates are flexible, then the interest rate should adjust so that the amount of saving and the amount
PDF CHAPTER Saving, Investment, 26 In both scenarios, public saving falls by $200 billion, and the budget deficit rises from $300 billion to $500 billion. 1. If consumers save the full $200 billion, national saving is unchanged, so investment is unchanged. 2. If consumers save $50 billion and spend $150 billion, then national saving and investment each fall by $150 billion.
Saving vs. Investing: Understanding the Key Differences Saving money typically means it is available when we need it and it has a low risk of losing value. Investing typically carries a long-term horizon, such as our children's college fund or...
In the saving investment diagram an increase in current ... 10) In the saving—investment diagram, an increase in current output would A) shift the saving curve to the left. B) shift the investment demand curve to the left. C) not shift the curves. D) shift the saving curve to the right. Answer: D
(PDF) saving investment practice | jingjing ma - Academia.edu Use the saving and investment identities from the National Income Accounts to answer the following questions. Suppose the following values are from the national income accounts of a country with a closed economy. (All values are in billions.) Y = $600 T = $100 C = $400 G = $120 a.
(d) Use the Saving-Investment diagram for a | Chegg.com Question: (d) Use the Saving-Investment diagram for a manufacturing based economy to analyze the effect on the real interest rate and quantity of savings and investment when (i) the government budget surplus increases and (ii) there is an improvement in technology in the manufacturing sector. Analyze each incident separately. (6 marks)
















Komentar
Posting Komentar